Differential pharmacology between the guinea-pig and the gorilla 5-HT1D receptor as probed with isochromans (5-HT1D-selective ligands)
- PMID: 10385247
- PMCID: PMC1566017
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702532
Differential pharmacology between the guinea-pig and the gorilla 5-HT1D receptor as probed with isochromans (5-HT1D-selective ligands)
Abstract
1. Both the 5-HT1D and 5-HT1B receptors are implicated in migraine pathophysiology. Recently isochromans have been discovered to bind primate 5-HT1D receptors with much higher affinity than 5-HT1B receptors. In the guinea-pig, a primary animal model for anti-migraine drug testing, however, isochromans bound the 5-HT1D receptor with lower affinity than the gorilla receptor. 2. This species-specific pharmacology was investigated, using site-directed mutagenesis on cloned guinea-pig receptors heterologously expressed in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. Mutations of threonine 100 and arginine 102 at the extracellular side of transmembrane II of the guinea-pig 5-HT1D receptor to the corresponding primate residues, isoleucine and histidine, respectively, enhanced its affinity for isochromans to that of the gorilla receptor, with little effects on its affinities for serotonin, sumatriptan and metergoline. Free energy change from the R102H mutation was about twice as much as that from the T100I mutation. 3. For G protein-coupling, serotonin marginally enhanced GTPgamma35S binding in membranes expressing the guinea-pig 5-HT1D receptor and its mutants, but robustly in membranes expressing the gorilla receptor. Sumatriptan enhanced GTPgamma35S binding in the latter nearly as much as serotonin, and several isochromans by 30-60% of serotonin. 4. We discovered key differences in the function and binding properties of guinea-pig and gorilla 5-HT1D receptors, and identified contributions of I100 and H102 of primate 5-HT1D receptors to isochroman binding. Among common experimental animals, only the rabbit shares I100 and H102 with primates, and could be useful for studying isochroman actions in vivo.
Figures
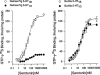
Similar articles
-
Molecular cloning and pharmacological characterization of guinea pig 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors.Neuropharmacology. 1997 Apr-May;36(4-5):513-24. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(97)00023-3. Neuropharmacology. 1997. PMID: 9225276
-
Characterization of ligand binding properties of the 5-HT1D receptors cloned from chimpanzee, gorilla and rhesus monkey in comparison with those from the human and guinea pig receptors.Neurosci Lett. 1997 Oct 17;235(3):117-20. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(97)00728-3. Neurosci Lett. 1997. PMID: 9406883
-
Agonistic properties of alniditan, sumatriptan and dihydroergotamine on human 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors expressed in various mammalian cell lines.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Apr;123(8):1655-65. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701766. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9605573 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT receptors mediating external carotid vasoconstriction in vagosympathectomized dogs.Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1999 Dec;20(12):1057-67. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1999. PMID: 11216445 Review.
-
A subfamily of 5-HT1D receptor genes.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Apr;13(4):152-9. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90053-9. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992. PMID: 1589909 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological profile of the 5-HT-induced inhibition of cardioaccelerator sympathetic outflow in pithed rats: correlation with 5-HT1 and putative 5-ht5A/5B receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Oct;140(4):725-35. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705489. Epub 2003 Sep 22. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14504136 Free PMC article.
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CX. Classification of Receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine; Pharmacology and Function.Pharmacol Rev. 2021 Jan;73(1):310-520. doi: 10.1124/pr.118.015552. Pharmacol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33370241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Donitriptan, but not sumatriptan, inhibits capsaicin-induced canine external carotid vasodilatation via 5-HT1B rather than 5-HT1D receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Sep;149(1):82-91. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706839. Epub 2006 Jul 31. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16880765 Free PMC article.
-
Acute migraine therapy: new drugs and new approaches.Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2011 Feb;13(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s11940-010-0105-6. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21110235 Free PMC article.
-
Post-triptan era for the treatment of acute migraine.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2004 Oct;8(5):393-8. doi: 10.1007/s11916-996-0013-3. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2004. PMID: 15361324 Review.
References
-
- ADHAM N., ROMANIENCO P., HART P., WEISHANK R.L., BRANCHEK T. The rat 5-hydroxytryptamine 1B receptor is the species homologue of the human 5-hydroxytryptamine 1D beta receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1992;41:1–7. - PubMed
-
- BOESS F.G., MARTIN I.L. Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors. Neuropharmacol. 1994;33:275–317. - PubMed
-
- BUZZI M.G., MOSKOWITZ M.A. Evidence for 5-HT1B/1D receptors mediating the anti-migraine effect of sumatriptan and dihydroergotamine. Cephalalgia. 1991;11:165–168. - PubMed
-
- BOUCHELET I., COHEN Z., CASE B., SEGUELA P., HAMEL E. Differential expression of sumatriptan-sensitive 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors in human trigeminal ganglia and cerebral blood vessels. Mol. Pharmacol. 1996;50:219–223. - PubMed
-
- CAEKEBEKE J.F.V., FERRARI M.D., ZWETSLOOT C.P., JANSEN J., SAXENA P.R. Anti-migraine drug sumatriptan increases blood flow velocity in large cerebral arteries during migraine attack. Neurology. 1992;42:1522–1526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

