Recombinant human erythropoietin inhibits iNOS activity and reverts vascular dysfunction in splanchnic artery occlusion shock
- PMID: 10385249
- PMCID: PMC1566014
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702521
Recombinant human erythropoietin inhibits iNOS activity and reverts vascular dysfunction in splanchnic artery occlusion shock
Abstract
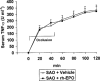
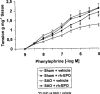
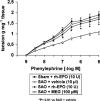
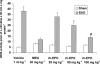
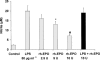
1. We investigated the effects of recombinant human erythropoietin (rh-EPO) in splanchnic artery occlusion (SAO) shock. Sham operated animals were used as controls. Survival rate, mean arterial blood pressure (MAP), serum Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF-alpha), plasma nitrite/nitrate concentrations, red blood cell (RBC) count, blood haemoglobin (Hb), the responsiveness of aortic rings to phenylephrine (PE, 1 nM-10 microM) and the activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) were studied. 2. SAO shocked rats had a decreased survival rate (0% at 4 h of reperfusion, while sham shocked rats survived more than 4 h), enhanced serum TNF-alpha concentrations, increased plasma nitrite/nitrate levels (60+/-9.5 microM; sham shocked rats= 2+/-0.4 microM), decreased MAP, unchanged RBC count and blood Hb and enhanced iNOS activity in the aorta. Moreover aortic rings from shocked rats showed a marked hyporeactivity to PE. 3. Rh-EPO (25, 50 and 100 U 100 g(-1), 5 min following the onset of reperfusion) increased survival rate (70% at 4 h of reperfusion with the highest dose), reduced plasma nitrite/nitrate concentrations (10.3+/-3.3 microM), increased MAP, did not change RBC count and blood Hb, and inhibited iNOS activity in thoracic aortae. Furthermore rh-EPO, either in vivo or in vitro (10 U for 1 h in the organ bath), restored to control values the hyporeactivity to PE. Finally rh-EPO inhibited the activity of iNOS in peritoneal macrophages activated with endotoxin. 4. Our data suggest that rh-EPO protects against SAO shock by inhibiting iNOS activity.
Figures
References
-
- ACQUIT C.H.I., FERRAGU-HAGUET M., LEFEBVRE A., BERTHELOT J.M., PETERLONGO F., CASTAINGNE J.P. Recombinant erythropoietin and blood pressure. Lancet. 1987;2:1083. - PubMed
-
- BUEMI M., ALLEGRA A., SQUADRITO F., BUEMI A.L., LAGANA' A., ALOISI C., FRISINA N. Effects of intravenous administration of recombinant human erythropoietin in rats subjected to hemorrhagic shock. Nephron. 1993;65:440–443. - PubMed
-
- CAPUTI A.P., ROSSI F., CARNEY K., BREZENOFF H.E. Modulatory effect of brain acetylcholine on reflex-induced bradycardia and tachycardia in conscious rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1980;215:309–316. - PubMed
-
- DING A.H., NATHAN C.F., STUEHR D.J. Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. J. Immunol. 1988;141:2407–2412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

