Synergistic effect with Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2 of the C-terminal of substance P and insulin-like growth factor-1 on epithelial wound healing of rabbit cornea
- PMID: 10385250
- PMCID: PMC1566023
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702550
Synergistic effect with Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2 of the C-terminal of substance P and insulin-like growth factor-1 on epithelial wound healing of rabbit cornea
Abstract
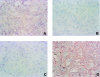
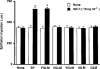
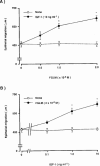
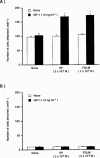
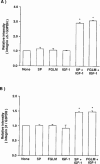
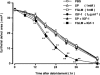
1. We previously reported that substance P and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) synergistically stimulate corneal epithelial wound healing in vitro and in vivo. We wished to identify which portion of the amino acid sequence of substance P might be responsible for this synergism. 2. Corneal epithelial migration was not affected by the addition of any one of the following factors: substance P; Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2 (C-terminal of substance P); Val-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2 (C-terminal of neurokinin A, neurokinin B, and kassinin); Tyr-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2 (C-terminal of physalaemin); Ile-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2 (C-terminal of eledoisin); or Gly-Leu-Met-NH2 (common C-terminal of tachykinins). 3. In the presence of IGF-1, only substance P and Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2 were synergistic in stimulating corneal epithelial migration in a dose-dependent fashion. 4. The combination of Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2 and IGF-1 did not affect the incorporation of [3H]-thymidine into corneal epithelial cells. 5. Treatment with Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2 and IGF-1, but not with Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2 or IGF-1 alone, increased attachment of corneal epithelial cells to a fibronectin matrix. 6. The levels of alpha5 and beta1 integrin were not affected by Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2 or IGF-1 alone, but they were significantly increased by the combination of Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2 and IGF-1. 7. Topical application of the same combination facilitated corneal epithelial wound closure in vivo. 8. These results demonstrated that Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2, a sequence of 4 amino-acids of the C-terminal of substance P, is the minimum sequence necessary to produce the synergistic effects of substance P and IGF-1 on corneal epithelial wound healing.
Figures
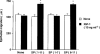

References
-
- ARAKI K., OHASHI Y., KINOSHITA S., HAYASHI K., KUWAYAMA Y., TANO Y. Epithelial wound healing in the denervated cornea. Curr. Eye Res. 1994;13:203–211. - PubMed
-
- BAKER K.S., ANDERSON S.C., ROMANOWSKI E.G., THOFT R.A., SUNDARRAJ N. Trigeminal ganglion neurons affect corneal epithelial phenotype. Influence on type VII collagen expression in vitro. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1993;34:137–144. - PubMed
-
- BROWN S.M., LAMBERTS D.W., REID T.W., NISHIDA T., MURPHY C.J. Neurotrophic and anhidrotic keratopathy treated with substance P and insulinlike growth factor 1. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1997;115:926–927. - PubMed
-
- BUTLER J.M., POWELL D., UNGER W.G. Substance P levels in normal and sensorily denervated rabbit eyes. Exp. Eye Res. 1980;30:311–313. - PubMed
-
- CINTRON C., HASSINGER L., KUBLIN C.L., FRIEND J. A simple method for the removal of rabbit corneal epithelium utilizing n-heptanol. Ophthalmic Res. 1979;11:90–96.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

