The zinc finger protein A20 inhibits TNF-induced NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression by interfering with an RIP- or TRAF2-mediated transactivation signal and directly binds to a novel NF-kappaB-inhibiting protein ABIN
- PMID: 10385526
- PMCID: PMC2133159
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.145.7.1471
The zinc finger protein A20 inhibits TNF-induced NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression by interfering with an RIP- or TRAF2-mediated transactivation signal and directly binds to a novel NF-kappaB-inhibiting protein ABIN
Abstract
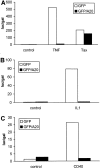
The zinc finger protein A20 is a tumor necrosis factor (TNF)- and interleukin 1 (IL-1)-inducible protein that negatively regulates nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB)-dependent gene expression. However, the molecular mechanism by which A20 exerts this effect is still unclear. We show that A20 does not inhibit TNF- induced nuclear translocation and DNA binding of NF-kappaB, although it completely prevents the TNF- induced activation of an NF-kappaB-dependent reporter gene, as well as TNF-induced IL-6 and granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor gene expression. Moreover, NF-kappaB activation induced by overexpression of the TNF receptor-associated proteins TNF receptor-associated death domain protein (TRADD), receptor interacting protein (RIP), and TNF recep- tor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) was also inhibited by expression of A20, whereas NF-kappaB activation induced by overexpression of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK) or the human T cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) Tax was unaffected. These results demonstrate that A20 inhibits NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression by interfering with a novel TNF-induced and RIP- or TRAF2-mediated pathway that is different from the NIK-IkappaB kinase pathway and that is specifically involved in the transactivation of NF-kappaB. Via yeast two-hybrid screening, we found that A20 binds to a novel protein, ABIN, which mimics the NF-kappaB inhibiting effects of A20 upon overexpression, suggesting that the effect of A20 is mediated by its interaction with this NF-kappaB inhibiting protein, ABIN.
Figures
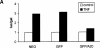
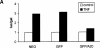

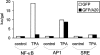
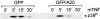
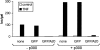

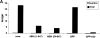
Similar articles
-
Identification of a novel A20-binding inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappa B activation termed ABIN-2.J Biol Chem. 2001 Aug 10;276(32):30216-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100048200. Epub 2001 Jun 4. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11390377
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 activates the JNK pathway through its extreme C terminus via a mechanism involving TRADD and TRAF2.J Virol. 1999 Feb;73(2):1023-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.2.1023-1035.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9882303 Free PMC article.
-
The cytokine-inducible zinc finger protein A20 inhibits IL-1-induced NF-kappaB activation at the level of TRAF6.FEBS Lett. 1999 Jan 15;442(2-3):147-50. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(98)01645-7. FEBS Lett. 1999. PMID: 9928991
-
ABINs: A20 binding inhibitors of NF-kappa B and apoptosis signaling.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Jul 15;78(2):105-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.02.009. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19464428 Review.
-
The biology of A20-binding inhibitors of NF-kappaB activation (ABINs).Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;809:13-31. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0398-6_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 25302363 Review.
Cited by
-
The Anti-Oxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Apoptotic, and Anti-Necroptotic Role of Zinc in COVID-19 and Sepsis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Oct 31;12(11):1942. doi: 10.3390/antiox12111942. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive map of the toll-like receptor signaling network.Mol Syst Biol. 2006;2:2006.0015. doi: 10.1038/msb4100057. Epub 2006 Apr 18. Mol Syst Biol. 2006. PMID: 16738560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-kappaB activation and zinc finger protein A20 expression in mature dendritic cells derived from liver allografts undergoing acute rejection.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Jun;9(6):1296-301. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1296. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12800244 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the NF-kappaB inhibitor ABIN-3 in response to TNF and toll-like receptor 4 stimulation is itself regulated by NF-kappaB.J Cell Mol Med. 2008 Jan-Feb;12(1):316-29. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00187.x. Epub 2007 Dec 10. J Cell Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18081698 Free PMC article.
-
A Supportive Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Insulin-Producing Langerhans Islets with a Specific Emphasis on The Secretome.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 18;11(9):2558. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092558. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37761001 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barnes PJ, Karin M. Nuclear factor-κB: a pivotal transcription factor in inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1066–1071. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann M, Hart L, Lindsay M, Barnes PJ, Newton R. IκB degradation and nuclear factor-κB DNA binding are insufficient for interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α induced κB-dependent transcription. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:6607–6610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

