Cdc53/cullin and the essential Hrt1 RING-H2 subunit of SCF define a ubiquitin ligase module that activates the E2 enzyme Cdc34
- PMID: 10385629
- PMCID: PMC316801
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.13.12.1614
Cdc53/cullin and the essential Hrt1 RING-H2 subunit of SCF define a ubiquitin ligase module that activates the E2 enzyme Cdc34
Abstract
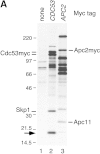
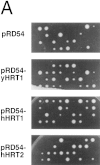
SCFCdc4 (Skp1, Cdc53/cullin, F-box protein) defines a family of modular ubiquitin ligases (E3s) that regulate diverse processes including cell cycle, immune response, and development. Mass spectrometric analysis of proteins copurifying with Cdc53 identified the RING-H2 finger protein Hrt1 as a subunit of SCF. Hrt1 shows striking similarity to the Apc11 subunit of anaphase-promoting complex. Conditional inactivation of hrt1(ts) results in stabilization of the SCFCdc4 substrates Sic1 and Cln2 and cell cycle arrest at G1/S. Hrt1 assembles into recombinant SCF complexes and individually binds Cdc4, Cdc53 and Cdc34, but not Skp1. Hrt1 stimulates the E3 activity of recombinant SCF potently and enables the reconstitution of Cln2 ubiquitination by recombinant SCFGrr1. Surprisingly, SCF and the Cdc53/Hrt1 subcomplex activate autoubiquitination of Cdc34 E2 enzyme by a mechanism that does not appear to require a reactive thiol. The highly conserved human HRT1 complements the lethality of hrt1Delta, and human HRT2 binds CUL-1. We conclude that Cdc53/Hrt1 comprise a highly conserved module that serves as the functional core of a broad variety of heteromeric ubiquitin ligases.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Cdc53 is a scaffold protein for multiple Cdc34/Skp1/F-box proteincomplexes that regulate cell division and methionine biosynthesis in yeast.Genes Dev. 1998 Mar 1;12(5):692-705. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.5.692. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9499404 Free PMC article.
-
F-box proteins are receptors that recruit phosphorylated substrates to the SCF ubiquitin-ligase complex.Cell. 1997 Oct 17;91(2):209-19. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80403-1. Cell. 1997. PMID: 9346238
-
Reconstitution of G1 cyclin ubiquitination with complexes containing SCFGrr1 and Rbx1.Science. 1999 Apr 23;284(5414):662-5. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5414.662. Science. 1999. PMID: 10213692
-
Proteolysis and the G1-S transition: the SCF connection.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998 Feb;8(1):36-42. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(98)80059-2. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998. PMID: 9529603 Review.
-
Proteolysis and the cell cycle: with this RING I do thee destroy.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2000 Feb;10(1):54-64. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(99)00049-0. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2000. PMID: 10679394 Review.
Cited by
-
CRL Ubiquitin Ligases and DNA Damage Response.Front Oncol. 2012 Apr 9;2:29. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00029. eCollection 2012. Front Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22655267 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation of Hof1 by SCF(Grr1) is important for actomyosin contraction during cytokinesis in yeast.EMBO J. 2005 Apr 6;24(7):1440-52. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600627. Epub 2005 Mar 17. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 15775961 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle-dependent expression of mammalian E2-C regulated by the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Aug;11(8):2821-31. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.8.2821. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10930472 Free PMC article.
-
CUL-4A is critical for early embryonic development.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;22(14):4997-5005. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.14.4997-5005.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12077329 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum degradation requires lumen to cytosol signaling. Transmembrane control of Hrd1p by Hrd3p.J Cell Biol. 2000 Oct 2;151(1):69-82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.1.69. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11018054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai C, Sen P, Hofmann K, Ma L, Goebl M, Harper JW, Elledge SJ. SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell. 1996;86:263–274. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee A, Gregori L, Xu Y, Chau V. The bacterially expressed yeast CDC34gene product can undergo autoubiquitination to form a multiubiquitin chain-linked protein. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:5668–5675. - PubMed
-
- Barral Y, Jentsch S, Mann C. G(1) cyclin turnover and nutrient-uptake are controlled by a common pathway in yeast. Genes & Dev. 1995;9:399–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
