Delineation of key amino acid side chains and peptide domains for antimicrobial properties of divercin V41, a pediocin-like bacteriocin secreted by Carnobacterium divergens V41
- PMID: 10388680
- PMCID: PMC91433
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.7.2895-2900.1999
Delineation of key amino acid side chains and peptide domains for antimicrobial properties of divercin V41, a pediocin-like bacteriocin secreted by Carnobacterium divergens V41
Abstract
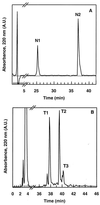
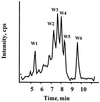
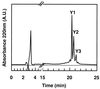
Divercin V41 (DV41) is a class IIa bacteriocin produced by Carnobacterium divergens V41. This antilisterial peptide is homologous to pediocin PA-1 and contains two disulfide bonds. To establish the structure-activity relationships of this specific family of bacteriocin, chemical modifications and enzymatic hydrolysis were performed on DV41. Alteration of the net charge of this cationic bacteriocin by succinylation and acetylation revealed that, in a certain range, the electrostatic interactions were surprisingly not necessary for the activity of DV41. Cleavage of DV41 by endoproteinase Asp-N released two fragments N1[1-17] and N2[18-43] corresponding to the conserved hydrophilic N-terminal and the variable hydrophobic C-terminal sequences, respectively. Inhibitory assays showed that only the C-terminal fragment was active, and after trypsin cleavage at Lys42 or disulfide reduction it lost its inhibitory activity. These results suggested that both hydrophobicity and folding imposed by the Cys25-Cys43 disulfide bond were essential for antilisterial activity of the C-terminal hydrophobic peptide. Chemical oxidation of tryptophan residues by N-bromosuccinimide demonstrated that these residues were crucial for inhibitory activity since modification of any one of them rendered DV41 inactive. On the contrary, only the modification of all the three tyrosine residues caused a total loss of antilisterial activity. These latter results strengthened previous results suggesting that the N-terminal domain containing the YGNGV consensus sequence was not involved in the binding of DV41 to a potential specific receptor on listerial cells.
Figures
References
-
- Bhugaloo-vial P, Dousset X, Metivier A, Sorokine O, Anglade P, Boyaval P, Marion D. Purification and amino acid sequences of piscicocins V1a and V1b, two class IIa bacteriocins secreted by Carnobacterium pisicola V1 that display significantly different levels of significantly different levels of specify. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1996;62:4410–4416. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blochet J E, Chevalier C, Forest E, Pebay-Peyroula E, Gautier M F, Joudrier P, Pézolet M, Marion D. Complete amino acid sequence of puroindoline, a new basic and cystine rich protein with a unique tryptophan-rich domain, isolated from wheat endosperm by Triton X-114 phase partitioning. FEBS Lett. 1993;329:336–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

