Formation of hyodeoxycholic acid from muricholic acid and hyocholic acid by an unidentified gram-positive rod termed HDCA-1 isolated from rat intestinal microflora
- PMID: 10388717
- PMCID: PMC91470
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.7.3158-3163.1999
Formation of hyodeoxycholic acid from muricholic acid and hyocholic acid by an unidentified gram-positive rod termed HDCA-1 isolated from rat intestinal microflora
Abstract
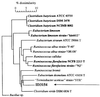
From the rat intestinal microflora we isolated a gram-positive rod, termed HDCA-1, that is a member of a not previously described genomic species and that is able to transform the 3alpha,6beta, 7beta-trihydroxy bile acid beta-muricholic acid into hyodeoxycholic acid (3alpha,6alpha-dihydroxy acid) by dehydroxylation of the 7beta-hydroxy group and epimerization of the 6beta-hydroxy group into a 6alpha-hydroxy group. Other bile acids that were also transformed into hyodeoxycholic acid were hyocholic acid (3alpha, 6alpha,7alpha-trihydroxy acid), alpha-muricholic acid (3alpha,6beta, 7alpha-trihydroxy acid), and omega-muricholic acid (3alpha,6alpha, 7beta-trihydroxy acid). The strain HDCA-1 could not be grown unless a nonconjugated 7-hydroxylated bile acid and an unidentified growth factor produced by a Ruminococcus productus strain that was also isolated from the intestinal microflora were added to the culture medium. Germfree rats selectively associated with the strain HDCA-1 plus a bile acid-deconjugating strain and the growth factor-producing R. productus strain converted beta-muricholic acid almost completely into hyodeoxycholic acid.
Figures

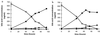
Similar articles
-
Influence of cholesterol feeding on liver microsomal metabolism of steroids and bile acids in conventional and germ-free rats.J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8496-502. J Biol Chem. 1975. PMID: 811655
-
Cooperative formation of omega-muricholic acid by intestinal microorganisms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):141-7. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.141-147.1983. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983. PMID: 6824314 Free PMC article.
-
Interfacial properties of most monofluorinated bile acids deviate markedly from the natural congeners: studies with the Langmuir-Pockels surface balance.J Lipid Res. 2005 Mar;46(3):571-81. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M400439-JLR200. Epub 2004 Dec 16. J Lipid Res. 2005. PMID: 15604514
-
Microbial bile acid transformation.Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Nov;27(11):1341-7. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.11.1341. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974. PMID: 4217103 Review. No abstract available.
-
Species-specific and age-dependent bile acid composition: aspects on CYP8B and CYP4A subfamilies in bile acid biosynthesis.Curr Drug Metab. 2008 May;9(4):323-31. doi: 10.2174/138920008784220574. Curr Drug Metab. 2008. PMID: 18473750 Review.
Cited by
-
Profiling of urinary bile acids in piglets by a combination of enzymatic deconjugation and targeted LC-MRM-MS.J Lipid Res. 2016 Oct;57(10):1917-1933. doi: 10.1194/jlr.D069831. Epub 2016 Aug 18. J Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 27538824 Free PMC article.
-
Fecal Hyodeoxycholic Acid Is Correlated With Tylosin-Induced Microbiome Changes in Growing Pigs.Front Vet Sci. 2018 Aug 28;5:196. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2018.00196. eCollection 2018. Front Vet Sci. 2018. PMID: 30211174 Free PMC article.
-
Iron overload reduces synthesis and elimination of bile acids in rat liver.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 5;9(1):9780. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46150-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31278332 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbial metabolite hyodeoxycholic acid targets the TLR4/MD2 complex to attenuate inflammation and protect against sepsis.Mol Ther. 2023 Apr 5;31(4):1017-1032. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.01.018. Epub 2023 Jan 24. Mol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36698311 Free PMC article.
-
The gut bacterium Extibacter muris produces secondary bile acids and influences liver physiology in gnotobiotic mice.Gut Microbes. 2021 Jan-Dec;13(1):1-21. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1854008. Gut Microbes. 2021. PMID: 33382950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borum M L, Shehan K L, Fromm H, Jahangeer S, Floor M K, Alabaster O. Fecal bile acid excretion and composition in response to changes in dietary wheat bran, fat and calcium in the rat. Lipids. 1992;27:999–1004. - PubMed
-
- Einarsson K. On the formation of hyodeoxycholic acid in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1966;241:534–539. - PubMed
-
- Eyssen H, De Pauw G, Parmentier G. Effect of lactose on Δ5-steroid-reducing activity of intestinal bacteria in gnotobiotic rats. J Nutr. 1974;104:605–612. - PubMed
-
- Eyssen H J, Parmentier G G, Mertens J A. Sulfated bile acids in germ-free and conventional mice. Eur J Biochem. 1976;66:507–514. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

