Characterization of methylglyoxal synthase from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 and its use in the formation of 1, 2-propanediol
- PMID: 10388730
- PMCID: PMC91483
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.7.3244-3247.1999
Characterization of methylglyoxal synthase from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 and its use in the formation of 1, 2-propanediol
Abstract
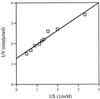
A gene encoding a putative 150-amino-acid methylglyoxal synthase was identified in Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. The enzyme was overexpressed in Escherichia coli and purified. Methylglyoxal synthase has a native molecular mass of 60 kDa and an optimum pH of 7.5. The Km and Vmax values for the substrate dihydroxyacetone phosphate were 0.53 mM and 1.56 mmol min(-1) microgram(-1), respectively. When E. coli glycerol dehydrogenase was coexpressed with methylglyoxal synthase in E. coli BL21(DE3), 3.9 mM 1,2-propanediol was produced.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of catalytic bases in the active site of Escherichia coli methylglyoxal synthase: cloning, expression, and functional characterization of conserved aspartic acid residues.Biochemistry. 1998 Jul 14;37(28):10074-86. doi: 10.1021/bi980409p. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9665712
-
Metabolic engineering of a 1,2-propanediol pathway in Escherichia coli.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999 Mar;65(3):1180-5. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.3.1180-1185.1999. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10049880 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, expression, and characterization of a novel methylglyoxal synthase from Thermus sp. strain GH5.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2010 Nov;162(6):1519-28. doi: 10.1007/s12010-010-8933-0. Epub 2010 Apr 25. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20419481
-
O-acetylhomoserine sulfhydrylase from Clostridium novyi. Cloning, expression of the gene and characterization of the enzyme.Protein Expr Purif. 2021 Apr;180:105810. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2020.105810. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Protein Expr Purif. 2021. PMID: 33338587
-
Production of 1,2-propanediol from glycerol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 Aug;21(8):846-53. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1103.03009. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21876375
Cited by
-
A novel hyperthermophilic methylglyoxal synthase: molecular dynamic analysis on the regional fluctuations.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 28;11(1):2538. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82078-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33510339 Free PMC article.
-
Does Gut Microbial Methylglyoxal Metabolism Impact Human Physiology?Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 21;14(7):763. doi: 10.3390/antiox14070763. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of the Reductive 1,3-Propanediol Pathway Triggers Production of 1,2-Propanediol for Sustained Glycerol Fermentation by Clostridium pasteurianum.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 Aug 15;82(17):5375-88. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01354-16. Print 2016 Sep 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27342556 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional portrait of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae during acute disease--potential strategies for survival and persistence in the host.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35549. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035549. Epub 2012 Apr 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22530048 Free PMC article.
-
Clostridium beijerinckii and Clostridium difficile detoxify methylglyoxal by a novel mechanism involving glycerol dehydrogenase.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001 May;67(5):2004-10. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.5.2004-2010.2001. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11319074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babel W, Hofmann K H. The conversion of triosephosphate via methylglyoxal, a bypass to the glycolytic sequence in methylotrophic yeasts? FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1981;10:133–136.
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Brownlee M, Cerami A. The biochemistry of the complication of diabetes mellitus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:385–432. - PubMed
-
- Cameron D C, Altaras N E, Hoffman M L, Shaw A J. Metabolic engineering of propanediol pathways. Biotechnol Prog. 1998;14:116–125. - PubMed
-
- Cao D, Fan S T, Chung S S M. Identification and characterization of a novel human aldose reductase-like gene. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:11429–11435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

