Effective treatment of acute and chronic murine tuberculosis with liposome-encapsulated clofazimine
- PMID: 10390215
- PMCID: PMC89336
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.43.7.1638
Effective treatment of acute and chronic murine tuberculosis with liposome-encapsulated clofazimine
Abstract
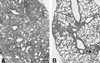
The therapeutic efficacy of liposomal clofazimine (L-CLF) was studied in mice infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis Erdman. Groups of mice were treated with either free clofazimine (F-CLF), L-CLF, or empty liposomes twice a week for five treatments beginning on day 1 (acute), day 21 (established), or day 90 (chronic) postinfection. One day after the last treatment, the numbers of CFU of M. tuberculosis in the spleen, liver, and lungs were determined. F-CLF at the maximum tolerated dose of 5 mg/kg of body weight was ineffective; however, 10-fold-higher doses of L-CLF demonstrated a dose response with significant CFU reduction in all tissues without any toxic effects. In acutely infected mice, 50 mg of L-CLF/kg reduced CFU 2 to 3 log units in all three organs. In established or chronic infection, treated mice showed no detectable CFU in the spleen or liver and 1- to 2-log-unit reduction in the lungs. A second series of L-CLF treatments cleared M. tuberculosis in all three tissues. L-CLF appears to be bactericidal in the liver and spleen, which remained negative for M. tuberculosis growth for 2 months. Thus, L-CLF could be useful in the treatment of tuberculosis.
Figures
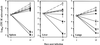



References
-
- Adams L B, Dinauer M C, Morgenstern D E, Krahenbuhl J L. Comparison of the roles of reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates in the host response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis using transgenic mice. Tuber Lung Dis. 1997;78:237–246. - PubMed
-
- Adams L B, Mason C M, Kolls J K, Scollard D, Krahenbuhl J L, Nelson S. Exacerbation of acute and chronic murine tuberculosis by administration of a TNF receptor-expressing adenovirus. J Infect Dis. 1995;171:400–405. - PubMed
-
- Bermudez L E. Use of liposomal preparations to treat mycobacterial infections. Immunobiology. 1994;191:578–583. - PubMed
-
- Bermudez L E M, Wu M, Young L S. Intracellular killing of Mycobacterium avium complex by rifapentine and liposome-encapsulated amikacin. J Infect Dis. 1987;156:510–513. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

