In vitro and in vivo activities of tea catechins against Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 10390246
- PMCID: PMC89367
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.43.7.1788
In vitro and in vivo activities of tea catechins against Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
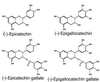
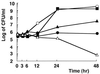
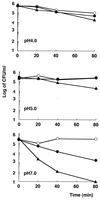
The catechin epigallocatechin gallate showed the strongest activity of the six tea catechins tested against Helicobacter pylori (MIC for 50% of the strains tested, 8 microg/ml). It had bactericidal activity at pH 7 but not at pH </=5.0. In infected Mongolian gerbils, H. pylori was eradicated in 10 to 36% of the catechin-treated animals, with significant decreases in mucosal hemorrhage and erosion. Tea catechins, therefore, may have therapeutic effects on H. pylori infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effect of green tea catechins in combination with sucralfate on Helicobacter pylori infection in Mongolian gerbils.J Gastroenterol. 2004 Jan;39(1):61-3. doi: 10.1007/s00535-003-1246-0. J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 14767736
-
A combination effect of epigallocatechin gallate, a major compound of green tea catechins, with antibiotics on Helicobacter pylori growth in vitro.Curr Microbiol. 2003 Sep;47(3):244-9. doi: 10.1007/s00284-002-3956-6. Curr Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14570277
-
Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of Chinese tea: in vitro study.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000 May;14(5):635-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00747.x. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000. PMID: 10792128
-
[Pharmacological study on the pathological changes of the gastric mucosa in Helicobacter pylori-infected Mongolian gerbils].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001 Oct;118(4):259-68. doi: 10.1254/fpj.118.259. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11680169 Review. Japanese.
-
Tea catechins as a potential alternative anti-infectious agent.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2007 Jun;5(3):497-506. doi: 10.1586/14787210.5.3.497. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2007. PMID: 17547513 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Green Tea Extract/Poly-γ-Glutamic Acid Complex in Obese Type 2 Diabetic Mice.Diabetes Metab J. 2013 Jun;37(3):196-206. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2013.37.3.196. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Diabetes Metab J. 2013. PMID: 23807923 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial activity of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L. red flower against antibiotic-resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori and identification of the flower constituents.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021 May 17;54(7):e10889. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2020e10889. eCollection 2021. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021. PMID: 34008759 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient inhibition of amyloid fibrillation and cytotoxicity of α-synuclein and human insulin using biosynthesized silver nanoparticles decorated by green tea polyphenols.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 16;14(1):3907. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54464-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38365968 Free PMC article.
-
Single GUV method reveals interaction of tea catechin (-)-epigallocatechin gallate with lipid membranes.Biophys J. 2007 May 1;92(9):3178-94. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.097105. Epub 2007 Feb 9. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17293394 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of epigallocatechin gallate on intestinal motility in mice.Environ Health Prev Med. 2003 May;8(2):47-51. doi: 10.1007/BF02897926. Environ Health Prev Med. 2003. PMID: 21432088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asaka M, Kimura T, Kudo M, Takeda H, Mitani S, Miyazaki T, Miki K, Graham D Y. Relationship of Helicobacter pylori to serum pepsinogens in an asymptomatic Japanese population. Gastroenterology. 1992;102:760–766. - PubMed
-
- Axon A T R, Moayyedi P. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori: omeprazole in combination with antibiotics. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1996;31(Suppl. 215):82–89. - PubMed
-
- Chiba N, Rao B V, Rademaker J W, Hunt R H. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of antibiotic therapy in eradicating Helicobacter pylori. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992;87:1716–1727. - PubMed
-
- Debets-Ossenkopp Y J, Namavar F, MacLaren D M. Effects of an acidic environment on the susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori to trospectomycin and other antimicrobial agents. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1995;14:353–355. - PubMed
-
- Goodwin C S, Blake P, Blincow E. The minimum inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations of antibiotics and anti-ulcer agents against Campylobacter pyloridis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986;17:309–314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

