A novel enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using the recombinant Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae ApxII antigen for diagnosis of pleuropneumonia in pig herds
- PMID: 10391878
- PMCID: PMC95743
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.6.4.630-632.1999
A novel enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using the recombinant Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae ApxII antigen for diagnosis of pleuropneumonia in pig herds
Abstract
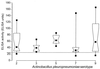
For the surveillance of pig herds infected with porcine pleuropneumonia, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using the recombinant Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae ApxII protein as species- but not serotype-specific antigen was developed. Using this ELISA, 243 of 400 animals from 22 A. pleuropneumoniae-infected herds were classified as seropositive.
Figures

References
-
- Butler J E, Heo Y, Adams P, Richardson H B. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): a measure of antibody concentration and affinity? Immunochemistry. 1978;15:131–146. - PubMed
-
- Fenwick B W, Henry S. Porcine pleuropneumonia. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1994;204:1334–1340. - PubMed
-
- Frey J. Virulence in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae and RTX toxins. Trends Microbiol. 1995;3:257–261. - PubMed
-
- Frey J, Bosse J T, Chang Y-F, Cullen J M, Fenwick B, Gerlach G-F, Gygi D, Haesenbrouck F, Inzana T J, Jansen R, Kamp E M, Segers J M, Smits M, Stenbaek E, Struck D K, Van den Bosch J F, Willson P J, Young R. Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae RTX-toxins: uniform designation of haemolysins, cytolysins, pleurotoxin and their genes. J Gen Microbiol. 1993;139:1723–1728. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

