Circulating immune complexes in IgA nephropathy consist of IgA1 with galactose-deficient hinge region and antiglycan antibodies
- PMID: 10393701
- PMCID: PMC408399
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI5535
Circulating immune complexes in IgA nephropathy consist of IgA1 with galactose-deficient hinge region and antiglycan antibodies
Abstract
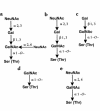
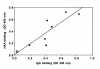
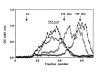
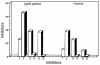
Circulating immune complexes (CICs) isolated from sera of patients with IgA nephropathy (IgAN) consist of undergalactosylated, mostly polymeric, and J chain-containing IgA1 and IgG antibodies specific for N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) residues in O-linked glycans of the hinge region of IgA1 heavy chains. Antibodies with such specificity occur in sera of IgAN patients, and in smaller quantities in patients with non-IgA proliferative glomerulonephritis and in healthy controls; they are present mainly in the IgG (predominantly IgG2 subclass), and less frequently in the IgA1 isotype. Their specificity for GalNAc was determined by reactivity with IgA1 myeloma proteins with enzymatically removed N-acetylneuraminic acid (NeuNAc) and galactose (Gal); removal of the O-linked glycans of IgA1 resulted in significantly decreased reactivity. Furthermore, IgA2 proteins that lack the hinge region with O-linked glycans but are otherwise structurally similar to IgA1 did not react with IgG or IgA1 antibodies. The re-formation of isolated and acid-dissociated CICs was inhibited more effectively by IgA1 lacking NeuNAc and Gal than by intact IgA1. Immobilized GalNAc and asialo-ovine submaxillary mucin (rich in O-linked glycans) were also effective inhibitors. Our results suggest that the deficiency of Gal in the hinge region of IgA1 molecules results in the generation of antigenic determinants containing GalNAc residues that are recognized by naturally occurring IgG and IgA1 antibodies.
Figures


References
-
- D’Amico G. The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world: IgA nephropathy. Q J Med. 1987;64:709–727. - PubMed
-
- Julian BA, Waldo FB, Rifai A, Mestecky J. IgA nephropathy, the most common glomerulonephritis worldwide. A neglected disease in the United States? Am J Med. 1988;84:129–132. - PubMed
-
- Galla JH. IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1995;47:377–387. - PubMed
-
- Russell MW, Mestecky J, Julian BA, Galla JH. IgA-associated renal diseases: antibodies to environmental antigens in sera and deposition of immunoglobulins and antigens in glomeruli. J Clin Immunol. 1986;6:74–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

