RNase P RNAs from some Archaea are catalytically active
- PMID: 10393902
- PMCID: PMC22142
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.14.7803
RNase P RNAs from some Archaea are catalytically active
Abstract
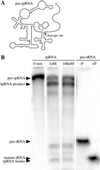
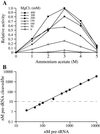
The RNA subunits of RNase Ps of Archaea and eukaryotes have been thought to depend fundamentally on protein for activity, unlike those of Bacteria that are capable of efficient catalysis in the absence of protein. Although the eukaryotic RNase P RNAs are quite different than those of Bacteria in both sequence and structure, the archaeal RNAs generally contain the sequences and structures of the bacterial, phylogenetically conserved catalytic core. A spectrum of archaeal RNase P RNAs were therefore tested for activity in a wide range of conditions. Many remain inactive in ionically extreme conditions, but catalytic activity could be detected from those of the methanobacteria, thermococci, and halobacteria. Chimeric holoenzymes, reconstituted from the Methanobacterium RNase P RNA and the Bacillus subtilis RNase P protein subunits, were functional at low ionic strength. The properties of the archaeal RNase P RNAs (high ionic-strength requirement, low affinity for substrate, and catalytic reconstitution by bacterial RNase P protein) are similar to synthetic RNase P RNAs that contain all of the catalytic core of the bacterial RNA but lack phylogenetically variable, stabilizing elements.
Figures



References
-
- Karwan R, Pluk H, van Venrooij W J, editors. Molecular Biology Reports Special Issue: RNase MRP/RNase P Systems. Vol. 22. Nijmegen: Kluwer; 1996.
-
- Reich C, Olsen G J, Pace B, Pace N R. Science. 1988;239:178–181. - PubMed
-
- Kurz J C, Niranjanakumari S, Fierke C A. Biochemistry. 1998;37:2393–2400. - PubMed
-
- Guerrier-Takada C, Gardner K, Marsh T, Pace N R, Altman S. Cell. 1983;35:849–857. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

