Mapmodulin, cytoplasmic dynein, and microtubules enhance the transport of mannose 6-phosphate receptors from endosomes to the trans-golgi network
- PMID: 10397758
- PMCID: PMC25434
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.7.2191
Mapmodulin, cytoplasmic dynein, and microtubules enhance the transport of mannose 6-phosphate receptors from endosomes to the trans-golgi network
Abstract
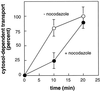
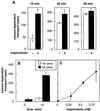
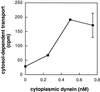
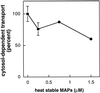
Late endosomes and the Golgi complex maintain their cellular localizations by virtue of interactions with the microtubule-based cytoskeleton. We study the transport of mannose 6-phosphate receptors from late endosomes to the trans-Golgi network in vitro. We show here that this process is facilitated by microtubules and the microtubule-based motor cytoplasmic dynein; transport is inhibited by excess recombinant dynamitin or purified microtubule-associated proteins. Mapmodulin, a protein that interacts with the microtubule-associated proteins MAP2, MAP4, and tau, stimulates the microtubule- and dynein-dependent localization of Golgi complexes in semi-intact Chinese hamster ovary cells. The present study shows that mapmodulin also stimulates the initial rate with which mannose 6-phosphate receptors are transported from late endosomes to the trans-Golgi network in vitro. These findings represent the first indication that mapmodulin can stimulate a vesicle transport process, and they support a model in which the microtubule-based cytoskeleton enhances the efficiency of vesicle transport between membrane-bound compartments in mammalian cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel assay reveals a role for soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion attachment protein in mannose 6-phosphate receptor transport from endosomes to the trans Golgi network.J Biol Chem. 1997 Oct 31;272(44):27737-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.44.27737. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9346916
-
Overexpression of the dynamitin (p50) subunit of the dynactin complex disrupts dynein-dependent maintenance of membrane organelle distribution.J Cell Biol. 1997 Oct 20;139(2):469-84. doi: 10.1083/jcb.139.2.469. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9334349 Free PMC article.
-
Mapmodulin: a possible modulator of the interaction of microtubule-associated proteins with microtubules.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 May 13;94(10):5084-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.10.5084. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9144194 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic dynein and early endosome transport.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Sep;72(17):3267-80. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1926-y. Epub 2015 May 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26001903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytoplasmic dynein and dynactin in cell division and intracellular transport.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;11(1):45-53. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(99)80006-4. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10047518 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin action on GLUT4 traffic visualized in single 3T3-l1 adipocytes by using ultra-fast microscopy.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Jan;12(1):129-41. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.1.129. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11160828 Free PMC article.
-
Rab9 GTPase regulates late endosome size and requires effector interaction for its stability.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Dec;15(12):5420-30. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-08-0747. Epub 2004 Sep 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15456905 Free PMC article.
-
The Golgi-associated hook3 protein is a member of a novel family of microtubule-binding proteins.J Cell Biol. 2001 Mar 5;152(5):923-34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.152.5.923. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11238449 Free PMC article.
-
Global detection of protein kinase D-dependent phosphorylation events in nocodazole-treated human cells.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 May;11(5):160-70. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.016014. Epub 2012 Apr 10. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22496350 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and characterization of LANP/pp32 null mice.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Apr;24(8):3140-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.8.3140-3149.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15060138 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

