Cellular biology of prion diseases
- PMID: 10398674
- PMCID: PMC100247
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.12.3.429
Cellular biology of prion diseases
Abstract
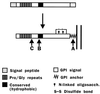
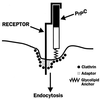
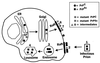
Prion diseases are fatal neurodegenerative disorders of humans and animals that are important because of their impact on public health and because they exemplify a novel mechanism of infectivity and biological information transfer. These diseases are caused by conformational conversion of a normal host glycoprotein (PrPC) into an infectious isoform (PrPSc) that is devoid of nucleic acid. This review focuses on the current understanding of prion diseases at the cell biological level. The characteristics of the diseases are introduced, and a brief history and description of the prion hypothesis are given. Information is then presented about the structure, expression, biosynthesis, and possible function of PrPC, as well as its posttranslational processing, cellular localization, and trafficking. The latest findings concerning PrPSc are then discussed, including cell culture systems used to generate this pathogenic isoform, the subcellular distribution of the protein, its membrane attachment, proteolytic processing, and its kinetics and sites of synthesis. Information is also provided on molecular models of the PrPC-->PrPSc conversion reaction and the possible role of cellular chaperones. The review concludes with suggestions of several important avenues for future investigation.
Figures


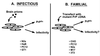



References
-
- Alper T, Cramp W A, Haig D A, Clarke M C. Does the agent of scrapie replicate without nucleic acid? Nature. 1967;214:764–766. - PubMed
-
- Anderson R G W. Plasmalemmal caveolae and GPI-anchored membrane proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993;5:647–652. - PubMed
-
- Anderson R M, Donnelly C A, Ferguson N M, Woolhouse M E J, Watt C J, Udy H J, MaWhinney S, Dunstan S P, Southwood M E J, Wilesmith J W, Ryan J B M, Hoinville L J, Hillerton J E, Austin A R, Wells G A H. Transmission dynamics and epidemiology of BSE in British cattle. Nature. 1996;382:779–788. - PubMed
-
- Arnold J E, Tipler C, Laszlo L, Hope J, Landon M, Mayer R J. The abnormal isoform of the prion protein accumulates in late-endosome-like organelles in scrapie-infected mouse brain. J Pathol. 1995;176:403–411. - PubMed
-
- Bamborough P, Wille H, Telling G C, Yehiely F, Prusiner S B, Cohen F E. Prion protein structure and scrapie replication: theoretical, spectroscopic, and genetic investigations. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol. 1996;61:495–509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

