Eikenella corrodens phase variation involves a posttranslational event in pilus formation
- PMID: 10400570
- PMCID: PMC93914
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.14.4154-4160.1999
Eikenella corrodens phase variation involves a posttranslational event in pilus formation
Abstract
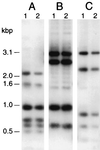
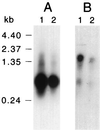
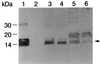
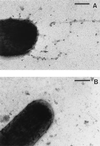
The human pathogen Eikenella corrodens synthesizes type IV pili and exhibits a phase variation involving the irreversible transition from piliated to nonpiliated variants. On solid medium, piliated variants form small (S-phase), corroding colonies whereas nonpiliated variants form large (L-phase), noncorroding colonies. We are studying the molecular basis of this phase variation in the clinical isolate E. corrodens VA1. A genomic fragment encoding the major type IV pilin was cloned from the S-phase variant of strain VA1. Sequence analysis of the fragment revealed four tandemly arranged potential open reading frames (ORFs), designated pilA1, pilA2, pilB, and hagA. Both pilA1 and pilA2 predict a type IV pilin. The protein predicted by pilB shares sequence identity with the Dichelobacter nodosus FimB fimbrial assembly protein. The protein predicted by hagA resembles a hemagglutinin. The region containing these four ORFs was designated the pilA locus. DNA hybridization and sequence analysis showed that the pilA locus of an L-phase variant of strain VA1 was identical to that of the S-phase variant. An abundant pilA1 transcript initiating upstream of pilA1 and terminating at a predicted hairpin structure between pilA1 and pilA2 was detected by several assays, as was a less abundant read-through transcript encompassing pilA1, pilA2, and pilB. Transcription from the pilA locus was nearly indistinguishable between S- and L-phase variants. Electron microscopy and immunochemical analysis showed that S-phase variants synthesize, export, and assemble pilin into pili. In contrast, L-phase variants synthesize pilin but do not export and assemble it into pili. These data suggest that a posttranslational event, possibly involving an alteration in pilin export and assembly, is responsible for phase variation in E. corrodens.
Figures
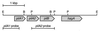
Similar articles
-
Role of the Eikenella corrodens pilA locus in pilus function and phase variation.J Bacteriol. 2001 Jan;183(1):55-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.1.55-62.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11114900 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmid-mediated genomic recombination at the pilin gene locus enhances the N-acetyl-D-galactosamine-specific haemagglutination activity and the growth rate of Eikenella corrodens.Microbiology (Reading). 2006 Mar;152(Pt 3):815-821. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28490-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2006. PMID: 16514161
-
The Ruminococcus albus pilA1-pilA2 locus: expression and putative role of two adjacent pil genes in pilus formation and bacterial adhesion to cellulose.Microbiology (Reading). 2005 Apr;151(Pt 4):1291-9. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27735-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2005. PMID: 15817796
-
Cloning and sequencing of two type 4 (N-methylphenylalanine) pilin genes from Eikenella corrodens.J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Mar;139(3):651-60. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-3-651. J Gen Microbiol. 1993. PMID: 8473871
-
Molecular strategies for fimbrial expression and assembly.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2001;12(2):101-15. doi: 10.1177/10454411010120020101. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2001. PMID: 11345521 Review.
Cited by
-
Empyema caused by eikenella corrodens.J Glob Infect Dis. 2011 Jul;3(3):303-5. doi: 10.4103/0974-777X.83546. J Glob Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21887067 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic variation in the plant pathogenic bacterium Acidovorax citrulli.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 2;8(9):e73189. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073189. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24023830 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Eikenella corrodens pilA locus in pilus function and phase variation.J Bacteriol. 2001 Jan;183(1):55-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.1.55-62.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11114900 Free PMC article.
-
Kingella kingae expresses type IV pili that mediate adherence to respiratory epithelial and synovial cells.J Bacteriol. 2008 Nov;190(21):7157-63. doi: 10.1128/JB.00884-08. Epub 2008 Aug 29. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18757541 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of type IV pili by Moraxella catarrhalis is essential for natural competence and is affected by iron limitation.Infect Immun. 2004 Nov;72(11):6262-70. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6262-6270.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15501752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alm R A, Mattick J S. Genes involved in the biogenesis and function of type-4 fimbriae in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Gene. 1997;192:89–98. - PubMed
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Ashimoto A, Chen C, Bakler I, Slots J. Polymerase chain reaction detection of 8 putative periodontal pathogens in subgingival plaque of gingivitis and advanced periodontal lesions. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1998;11:226–273. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons; 1989.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

