Glucose transport in the extremely thermoacidophilic Sulfolobus solfataricus involves a high-affinity membrane-integrated binding protein
- PMID: 10400586
- PMCID: PMC93930
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.14.4285-4291.1999
Glucose transport in the extremely thermoacidophilic Sulfolobus solfataricus involves a high-affinity membrane-integrated binding protein
Abstract
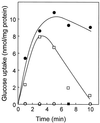
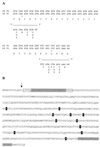
The archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus grows optimally at 80 degrees C and pH 2.5 to 3.5 on carbon sources such as yeast extracts, tryptone, and various sugars. Cells rapidly accumulate glucose. This transport activity involves a membrane-bound glucose-binding protein that interacts with its substrate with very high affinity (Kd of 0. 43 microM) and retains high glucose affinity at very low pH values (as low as pH 0.6). The binding protein was extracted with detergent and purified to homogeneity as a 65-kDa glycoprotein. The gene coding for the binding protein was identified in the S. solfataricus P2 genome by means of the amino-terminal amino acid sequence of the purified protein. Sequence analysis suggests that the protein is anchored to the membrane via an amino-terminal transmembrane segment. Neighboring genes encode two membrane proteins and an ATP-binding subunit that are transcribed in the reverse direction, whereas a homologous gene cluster in Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3 was found to be organized in an operon. These data indicate that S. solfataricus utilizes a binding-protein-dependent ATP-binding cassette transporter for the uptake of glucose.
Figures




References
-
- Albers S-V, Konings W N, Driessen A J M. A unique short signal sequence in membrane anchored proteins of Archaea. Mol Microbiol. 1999;30:1595–1596. - PubMed
-
- Brock T D, Brock K M, Belly R T, Weiss R L. Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and high temperature. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84:54–68. - PubMed
-
- Cusdin F S, Robinson M J, Holman G D, Hough D W, Danson M J. Characterisation of glucose transport in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus. FEBS Lett. 1996;387:193–195. - PubMed
-
- Essenberg R C, Candler C, Nida S K. Brucella abortus strain 2308 putative glucose and galactose transporter gene: cloning and characterization. Microbiology. 1997;143:1549–1555. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

