Genetic organization of the citCDEF locus and identification of mae and clyR genes from Leuconostoc mesenteroides
- PMID: 10400601
- PMCID: PMC93945
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.14.4411-4416.1999
Genetic organization of the citCDEF locus and identification of mae and clyR genes from Leuconostoc mesenteroides
Abstract
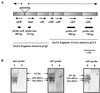
In this paper, we describe two open reading frames coding for a NAD-dependent malic enzyme (mae) and a putative regulatory protein (clyR) found in the upstream region of citCDEFG of Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. cremoris 195. The transcriptional analysis of the citrate lyase locus revealed one polycistronic mRNA covering the mae and citCDEF genes. This transcript was detected only on RNA prepared from cells grown in the presence of citrate. Primer extension experiments suggest that clyR and the citrate lyase operon are expressed from a bidirectional A-T-rich promoter region located between mae and clyR.
Figures



References
-
- Bott M, Dimroth P. Klebsiella pneumoniae genes for citrate lyase and citrate lyase ligase: localization, sequencing and expression. Mol Microbiol. 1994;14:347–356. - PubMed
-
- Bott M, Meyer M, Dimroth P. Regulation of anaerobic citrate metabolism in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18:533–546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

