The human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncoprotein can down-regulate p53 activity by targeting the transcriptional coactivator CBP/p300
- PMID: 10400710
- PMCID: PMC112697
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.8.6209-6219.1999
The human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncoprotein can down-regulate p53 activity by targeting the transcriptional coactivator CBP/p300
Abstract
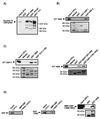
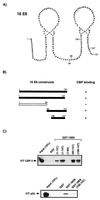
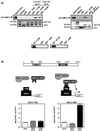
The transforming proteins of the small DNA tumor viruses, simian virus 40 (SV40), adenovirus, and human papillomavirus (HPV) target a number of identical cellular regulators whose functional abrogation is required for transformation. However, while both adenovirus E1A and SV40 large T transforming properties also depend on the targeting of the transcriptional coactivator CBP/p300, no such interaction has been described for the HPV oncoprotein E6 or E7. Here, we demonstrate that the HPV-16 E6 protein, previously shown to facilitate the degradation of p53 in a complex with E6-associated protein (E6AP), also targets CBP/p300 in an interaction involving the C-terminal zinc finger of E6 and CBP residues 1808 to 1826. Furthermore, this interaction is limited to E6 proteins of high-risk HPVs associated with cervical cancer that have the capacity to repress p53-dependent transcription. An HPV-16 E6 mutant (L50G) that binds CBP/p300, but not E6AP, is still capable of down-regulating p53 transcriptional activity. Thus, HPV E6 proteins possess two distinct mechanisms by which to abrogate p53 function: the repression of p53 transcriptional activity by targeting the p53 coactivator CBP/p300, and the removal of cellular p53 protein through the proteosome degradation pathway.
Figures


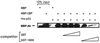
Similar articles
-
E6 oncoprotein represses p53-dependent gene activation via inhibition of protein acetylation independently of inducing p53 degradation.Mol Cell. 2005 Jan 21;17(2):251-64. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.12.016. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15664194
-
Complementation of a p300/CBP defective-binding mutant of adenovirus E1a by human papillomavirus E6 proteins.J Gen Virol. 2002 Apr;83(Pt 4):829-833. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-83-4-829. J Gen Virol. 2002. PMID: 11907332
-
Down regulation of the interleukin-8 promoter by human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 through effects on CREB binding protein/p300 and P/CAF.J Virol. 2002 Sep;76(17):8710-21. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.17.8710-8721.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12163591 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular targets of the oncoproteins encoded by the cancer associated human papillomaviruses.Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1991;22:239-48. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1991. PMID: 1668886 Review.
-
The role of TP53 in Cervical carcinogenesis.Hum Mutat. 2003 Mar;21(3):307-12. doi: 10.1002/humu.10178. Hum Mutat. 2003. PMID: 12619117 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Viral Ribonucleoproteins in Human Papillomavirus Type 16 Gene Expression.Viruses. 2020 Sep 30;12(10):1110. doi: 10.3390/v12101110. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33007936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basic mechanisms of high-risk human papillomavirus-induced carcinogenesis: roles of E6 and E7 proteins.Cancer Sci. 2007 Oct;98(10):1505-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00546.x. Epub 2007 Jul 23. Cancer Sci. 2007. PMID: 17645777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human papillomavirus E6 and Myc proteins associate in vivo and bind to and cooperatively activate the telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jul 8;100(14):8211-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1435900100. Epub 2003 Jun 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12821782 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the mechanisms of HPV E6 mutations in the destabilization of E6/E6AP/p53 complex.Biophys J. 2022 May 3;121(9):1704-1714. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.03.030. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Biophys J. 2022. PMID: 35364103 Free PMC article.
-
HPV E6 inhibits E6AP to regulate epithelial homeostasis by modulating keratinocyte differentiation commitment and YAP1 activation.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Jun 28;19(6):e1011464. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011464. eCollection 2023 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37379354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ait-Si-Ali S, Ramirez S, Barre F X, Dkhissi F, Magnaghi-Jaulin L, Girault J A, Robin P, Knibiehler M, Pritchard L L, Ducommun B, Trouche D, Harel-Bellan A. Histone acetyltransferase activity of CBP is controlled by cycle-dependent kinases and oncoprotein E1A. Nature. 1998;396:184–186. - PubMed
-
- Arany Z, Newsome D, Oldread E, Livingston D M, Eckner R. A family of transcriptional adapter proteins targeted by the E1A oncoprotein. Nature. 1995;374:81–84. - PubMed
-
- Avantaggiati M L, Ogryzko V, Gardner K, Giordano A, Levine A S, Kelly K. Recruitment of p300/CBP in p53-dependent signal pathways. Cell. 1997;89:1175–1184. - PubMed
-
- Bagchi S, Raychaudhuri P, Nevins J R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990;62:659–669. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

