The human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncoprotein can down-regulate p53 activity by targeting the transcriptional coactivator CBP/p300
- PMID: 10400710
- PMCID: PMC112697
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.8.6209-6219.1999
The human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncoprotein can down-regulate p53 activity by targeting the transcriptional coactivator CBP/p300
Abstract
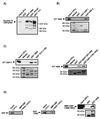
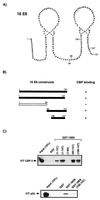
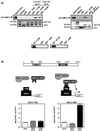
The transforming proteins of the small DNA tumor viruses, simian virus 40 (SV40), adenovirus, and human papillomavirus (HPV) target a number of identical cellular regulators whose functional abrogation is required for transformation. However, while both adenovirus E1A and SV40 large T transforming properties also depend on the targeting of the transcriptional coactivator CBP/p300, no such interaction has been described for the HPV oncoprotein E6 or E7. Here, we demonstrate that the HPV-16 E6 protein, previously shown to facilitate the degradation of p53 in a complex with E6-associated protein (E6AP), also targets CBP/p300 in an interaction involving the C-terminal zinc finger of E6 and CBP residues 1808 to 1826. Furthermore, this interaction is limited to E6 proteins of high-risk HPVs associated with cervical cancer that have the capacity to repress p53-dependent transcription. An HPV-16 E6 mutant (L50G) that binds CBP/p300, but not E6AP, is still capable of down-regulating p53 transcriptional activity. Thus, HPV E6 proteins possess two distinct mechanisms by which to abrogate p53 function: the repression of p53 transcriptional activity by targeting the p53 coactivator CBP/p300, and the removal of cellular p53 protein through the proteosome degradation pathway.
Figures


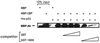
References
-
- Ait-Si-Ali S, Ramirez S, Barre F X, Dkhissi F, Magnaghi-Jaulin L, Girault J A, Robin P, Knibiehler M, Pritchard L L, Ducommun B, Trouche D, Harel-Bellan A. Histone acetyltransferase activity of CBP is controlled by cycle-dependent kinases and oncoprotein E1A. Nature. 1998;396:184–186. - PubMed
-
- Arany Z, Newsome D, Oldread E, Livingston D M, Eckner R. A family of transcriptional adapter proteins targeted by the E1A oncoprotein. Nature. 1995;374:81–84. - PubMed
-
- Avantaggiati M L, Ogryzko V, Gardner K, Giordano A, Levine A S, Kelly K. Recruitment of p300/CBP in p53-dependent signal pathways. Cell. 1997;89:1175–1184. - PubMed
-
- Bagchi S, Raychaudhuri P, Nevins J R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990;62:659–669. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

