Both memory and CD45RA+/CD62L+ naive CD4(+) T cells are infected in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals
- PMID: 10400736
- PMCID: PMC112723
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.8.6430-6435.1999
Both memory and CD45RA+/CD62L+ naive CD4(+) T cells are infected in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals
Abstract
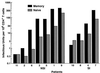
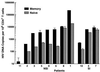
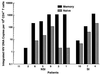
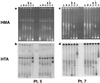
Cellular activation is critical for the propagation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection. It has been suggested that truly naive CD4(+) T cells are resistant to productive HIV-1 infection because of their constitutive resting state. Memory and naive CD4(+) T-cell subsets from 11 HIV-1-infected individuals were isolated ex vivo by a combination of magnetic bead depletion and fluorescence-activated cell sorting techniques with stringent criteria of combined expression of CD45RA and CD62L to identify naive CD4(+) T-cell subsets. In all patients HIV-1 provirus could be detected within naive CD45RA+/CD62L+ CD4(+) T cells; in addition, replication-competent HIV-1 was isolated from these cells upon CD4(+) T-cell stimulation in tissue cultures. Memory CD4(+) T cells had a median of fourfold more replication-competent virus and a median of sixfold more provirus than naive CD4(+) T cells. Overall, there was a median of 16-fold more integrated provirus identified in memory CD4(+) T cells than in naive CD4(+) T cells within a given patient. Interestingly, there was a trend toward equalization of viral loads in memory and naive CD4(+) T-cell subsets in those patients who harbored CXCR4-using (syncytium-inducing) viruses. Within any given patient, there was no selective usage of a particular coreceptor by virus isolated from memory versus naive CD4(+) T cells. Our findings suggest that naive CD4(+) T cells may be a significant viral reservoir for HIV, particularly in those patients harboring CXCR4-using viruses.
Figures

References
-
- Akbar A, Terry L, Timms A, Beverley P, Janossy G. Loss of CD45R and gain of UCHL1 reactivity is a feature of primed T cells. J Immunol. 1988;140:2171–2178. - PubMed
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder C C, Feng Y, Kennedy P E, Murphy P M, Berger E A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Cayota A, Vuillier F, Scott-Algara D, Dighiera G. Preferential replication of HIV-1 in memory CD4+ subpopulation. Lancet. 1990;336:941–942. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

