Expression of mouse mammary tumor virus superantigen mRNA in the thymus correlates with kinetics of self-reactive T-cell loss
- PMID: 10400761
- PMCID: PMC112748
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.8.6634-6645.1999
Expression of mouse mammary tumor virus superantigen mRNA in the thymus correlates with kinetics of self-reactive T-cell loss
Abstract
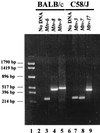
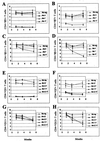
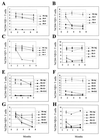
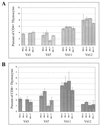
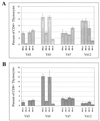
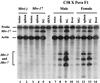
Mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) encodes a superantigen (Sag) that is expressed at the surface of antigen-presenting cells in conjunction with major histocompatibility complex (MHC) type II molecules. The Sag-MHC complex is recognized by entire subsets of T cells, leading to cytokine release and amplification of infected B and T cells that carry milk-borne MMTV to the mammary gland. Expression of Sag proteins from endogenous MMTV proviruses carried in the mouse germ line usually results in the deletion of self-reactive T cells during negative selection in the thymus and the elimination of T cells required for infection by specific milk-borne MMTVs. However, other endogenous MMTVs are unable to eliminate Sag-reactive T cells in newborn mice and cause partial loss of reactive T cells in adults. To investigate the kinetics of Sag-reactive T-cell deletion, backcross mice that contain single or multiple MMTVs were screened by a novel PCR assay designed to distinguish among highly related MMTV strains. Mice that contained Mtv-17 alone showed slow kinetics of reactive T-cell loss that involved the CD4(+), but not the CD8(+), subset. Deletion of CD4(+) or CD8(+) T cells reactive with Mtv-17 Sag was not detected in thymocytes. Slow kinetics of peripheral T-cell deletion by Mtv-17 Sag also was accompanied by failure to detect Mtv-17 sag-specific mRNA in the thymus, despite detectable expression in other tissues, such as spleen. Together, these data suggest that Mtv-17 Sag causes peripheral, rather than intrathymic, deletion of T cells. Interestingly, the Mtv-8 provirus caused partial deletion of CD4(+)Vbeta12(+) cells in the thymus, but other T-cell subsets appeared to be deleted only in the periphery. Our data have important implications for the level of antigen expression required for elimination of self-reactive T cells. Moreover, these experiments suggest that mice expressing endogenous MMTVs that lead to slow kinetics of T-cell deletion will be susceptible to infection by milk-borne MMTVs with the same Sag specificity.
Figures

References
-
- Abe R, Foo-Phillips M, Granger L G, Kanagawa O. Characterization of the Mlsf system. I. A novel “polymorphism” of endogenous superantigens. J Immunol. 1992;149:3429–3439. - PubMed
-
- Abe R, Kanagawa O, Sheard M A, Malissen B, Foo-Phillips M. Characterization of a new minor lymphocyte stimulatory system. I. Cluster of self antigens recognized by “I-E-reactive” Vβs, Vβ5, Vβ11, and Vβ12 T cell receptors for antigen. J Immunol. 1991;147:739–749. - PubMed
-
- Acha-Orbea H, Held W, Waanders G A, Shakhov A N, Scarpellino L, Lees R K, MacDonald H R. Exogenous and endogenous mouse mammary tumor virus superantigens. Immunol Rev. 1993;131:5–25. - PubMed
-
- Acha-Orbea H, MacDonald H R. Superantigens of mouse mammary tumor virus. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:459–486. - PubMed
-
- Acha-Orbea H, Shakhov A N, Scarpellino L, Kolb E, Muller V, Vessaz-Shaw A, Fuchs R, Blochlinger K, Rollini P, Billotte J, et al. Clonal deletion of Vβ14-bearing T cells in mice transgenic for mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1991;350:207–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

