Identification of a spliced gene from Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encoding a protein with similarities to latent membrane proteins 1 and 2A of Epstein-Barr virus
- PMID: 10400794
- PMCID: PMC112781
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.8.6953-6963.1999
Identification of a spliced gene from Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encoding a protein with similarities to latent membrane proteins 1 and 2A of Epstein-Barr virus
Abstract
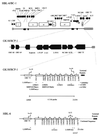
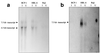
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) or human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8) is a novel herpesvirus implicated as the causative agent of Kaposi's sarcoma (KS), primary effusion lymphoma, and some cases of multicentric Castleman's disease. KSHV persists in the majority of KS spindle (endothelial tumor) cells and lymphoid cells in a latent form, with only a limited set of viral genes expressed in a tissue-specific manner. Here, we report the identification of a family of alternatively-spliced transcripts of approximately 7.5 kb expressed in latently infected body cavity-based lymphoma (BCBL) cell lines which are predicted to encode membrane proteins with similarities to the LMP2A and LMP1 proteins of Epstein-Barr virus. In two highly divergent sequence variants of the right end of the KSHV genome, alternative splicing of eight exons located between KSHV ORF 75 and the terminal repeats yields transcripts appropriate for proteins with up to 12 transmembrane domains, followed by a hydrophilic C-terminal, presumably cytoplasmic, domain. This C-terminal domain contains several YxxI/L motifs reminiscent of LMP2A and a putative TRAF binding site as in LMP1. In latently (persistently) infected BCBL cells the predominant transcript utilizes all eight exons, whereas in phorbol-ester-induced cells, a shorter transcript, lacking exons 4 and 5, is also abundant. We also found evidence for an alternative use of exon 1. Transfection of an epitope-tagged cDNA construct containing all exons indicates that the encoded protein is localized on cell surface and intracellular membranes, and glutathione S-transferase pull-down experiments indicate that its cytoplasmic domain, like that of LMP1, interacts with TRAF1, -2, and -3. Two of 20 KS patients had antibodies to the hydrophilic C-terminal domain, suggesting that the protein is expressed in vivo.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kappaB pathways by a Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K15 membrane protein.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(17):9346-58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9346-9358.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12915550 Free PMC article.
-
A single 13-kilobase divergent locus in the Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) genome contains nine open reading frames that are homologous to or related to cellular proteins.J Virol. 1997 Mar;71(3):1963-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.3.1963-1974.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9032328 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription pattern of human herpesvirus 8 open reading frame K3 in primary effusion lymphoma and Kaposi's sarcoma.J Virol. 2001 Aug;75(15):7161-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.15.7161-7174.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11435597 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological Features of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1045:357-376. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7230-7_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29896675 Review.
-
The pleiotropic effects of Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus.J Pathol. 2006 Jan;208(2):187-98. doi: 10.1002/path.1904. J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16362980 Review.
Cited by
-
New genes from old: redeployment of dUTPase by herpesviruses.J Virol. 2005 Oct;79(20):12880-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.20.12880-12892.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16188990 Free PMC article.
-
Array-based transcript profiling and limiting-dilution reverse transcription-PCR analysis identify additional latent genes in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.J Virol. 2010 Jun;84(11):5565-73. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02723-09. Epub 2010 Mar 10. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20219929 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular localization map of human herpesvirus 8 proteins.J Virol. 2008 Feb;82(4):1908-22. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01716-07. Epub 2007 Dec 12. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18077714 Free PMC article.
-
A systems biology approach to identify the combination effects of human herpesvirus 8 genes on NF-kappaB activation.J Virol. 2009 Mar;83(6):2563-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01512-08. Epub 2009 Jan 7. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19129458 Free PMC article.
-
The M type K15 protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus regulates microRNA expression via its SH2-binding motif to induce cell migration and invasion.J Virol. 2009 Jan;83(2):622-32. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00869-08. Epub 2008 Oct 29. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 18971265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambroziak J A, Blackbourn D J, Herndier B G, Glogau R G, Gullett J H, McDonald A R, Lennette E T, Levy J A. Herpes-like sequences in HIV-infected and uninfected Kaposi’s sarcoma patients. Science. 1995;268:582–583. - PubMed
-
- Auradé, F., and T. Schulz. Unpublished data.
-
- Beral V. Epidemiology of Kaposi’s sarcoma. In: Beral V, Jaffe H W, Weiss R A, editors. Cancer, HIV, and AIDS, cancer surveys. Vol. 10. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1991. pp. 5–22.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

