Cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA load is an independent predictor of CMV disease and survival in advanced AIDS
- PMID: 10400803
- PMCID: PMC112790
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.8.7027-7030.1999
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA load is an independent predictor of CMV disease and survival in advanced AIDS
Abstract
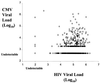
The impact of cytomegalovirus (CMV) on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) disease progression has been controversial. In this study, we sought to determine if CMV viral load is independent of HIV-1 viral load in predicting CMV disease and survival. Our findings indicate that in patients with advanced AIDS, CMV DNA load is an independent marker of CMV disease and survival and is more predictive than HIV-1 RNA load. Moreover, patients who respond to preemptive therapy with oral ganciclovir, with resulting undetectable levels of CMV DNA, in their plasma, have a significantly lower risk of developing CMV disease and higher rates of survival, despite stable or increasing HIV-1 RNA loads. These data provide support for CMV as an independent risk factor for mortality in persons with advanced AIDS and further suggest that effective preemptive therapy for CMV can improve patient survival rates.
Figures
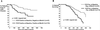
References
-
- Bowen E F, Wilson P, Cope A, Sabin C, Griffiths P, Davey C, Johnson M, Emery V. Cytomegalovirus retinitis in AIDS patients: influence of cytomegaloviral load on response to ganciclovir, time to recurrence and survival. AIDS. 1996;10:1515–1520. - PubMed
-
- Bowen E F, Sabin C A, Wilson P, Griffiths P D, Davey C C, Johnson M A, Emery V C. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) viraemia detected by polymerase chain reaction identifies a group of HIV-positive patients at high risk of CMV disease. AIDS. 1997;11:889–893. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-infected adults and adolescents. Morbid Mortal Weekly Rep. 1998;47(IRR-5):39–82.
-
- Cox D R, Oakes D. Analysis of survival data. London, England: Chapman and Hall; 1984.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

