STAT6-deficient mice exhibit normal induction of murine AIDS and expression of immunoglobulin E following infection with LP-BM5 murine leukemia viruses
- PMID: 10400816
- PMCID: PMC112803
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.8.7093-7095.1999
STAT6-deficient mice exhibit normal induction of murine AIDS and expression of immunoglobulin E following infection with LP-BM5 murine leukemia viruses
Abstract
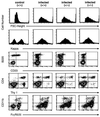
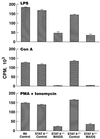
The unique Gag polyprotein of the replication-defective virus responsible for murine AIDS (MAIDS) induces B-cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation, including immunoglobulin class switch-recombination to immunoglobulin E (IgE). Secretion of IgE normally requires the serial induction of interleukin 4 (IL-4), engagement of the IL-4 receptor, activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 6, and induction of Iepsilon germline transcripts as a prelude to switching. Remarkably, expression of IgE is equivalent in normal and IL-4-deficient mice with MAIDS (Morawetz et al., J. Exp. Med. 184:1651-1661, 1996). To understand this anomaly, we studied mice with a null mutation of STAT6. Lymphoproliferation and immunodeficiency, the hallmarks of MAIDS, developed with comparable kinetics and degree in normal and mutant mice. In addition, serum IgE levels were indistinguishable in mice of either genotype. We conclude that B cells from mice with MAIDS activate unique IL-4- and STAT6-independent signaling pathways for B-cell activation and differentiation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD19 signaling pathways play a major role for murine AIDS induction and progression.J Immunol. 2002 Nov 15;169(10):5607-14. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.10.5607. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12421939
-
Effects of exogenous, nonleukemogenic, ecotropic murine leukemia virus infections on the immune systems of adult C57BL/6 mice.J Virol. 1995 Jul;69(7):4182-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.7.4182-4188.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7769677 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin (IL)-4-independent immunoglobulin class switch to immunoglobulin (Ig)E in the mouse.J Exp Med. 1996 Nov 1;184(5):1651-61. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.5.1651. J Exp Med. 1996. PMID: 8920855 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for a continued requirement for CD40/CD40 ligand (CD154) interactions in the progression of LP-BM5 retrovirus-induced murine AIDS.Virology. 1998 Feb 15;241(2):260-8. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8970. Virology. 1998. PMID: 9499800
-
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes to endogenous mouse retroviruses and mechanisms of retroviral escape.Immunol Rev. 1999 Apr;168:271-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01298.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10399080 Review.
Cited by
-
Dendritic cell-CD4+ T cell interaction: The differential role of IL-4/IL-13 in serum IgE levels in house dust mite allergic patients.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jan;21(1):95. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9527. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33363606 Free PMC article.
-
Janus kinases and signal transducers and activators of transcription: their roles in cytokine signaling, development and immunoregulation.Arthritis Res. 2000;2(1):16-32. doi: 10.1186/ar66. Epub 1999 Dec 23. Arthritis Res. 2000. PMID: 11094415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutathione Depletion Is Linked with Th2 Polarization in Mice with a Retrovirus-Induced Immunodeficiency Syndrome, Murine AIDS: Role of Proglutathione Molecules as Immunotherapeutics.J Virol. 2016 Jul 27;90(16):7118-7130. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00603-16. Print 2016 Aug 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27226373 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-4 up-regulates mouse mammary tumor virus expression yet is not required for in vivo virus spread.J Virol. 2001 Dec;75(23):11886-90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.23.11886-11890.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11689671 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the CD154-positive and CD40-positive cellular subsets required for pathogenesis in retrovirus-induced murine immunodeficiency.J Virol. 2001 Apr;75(8):3581-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.8.3581-3589.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11264347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gazzinelli R T, Makino M, Chattopadhyay S K, Snapper C M, Sher A, Hügin A W, Morse H C., III CD4+ subset regulation in viral infection. J Immunol. 1992;148:182–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

