A visual screen of a GFP-fusion library identifies a new type of nuclear envelope membrane protein
- PMID: 10402458
- PMCID: PMC2199743
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.146.1.29
A visual screen of a GFP-fusion library identifies a new type of nuclear envelope membrane protein
Abstract
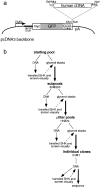
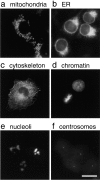
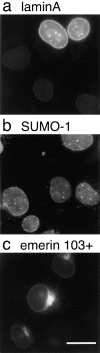
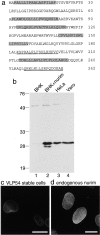
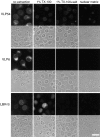
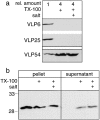
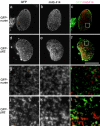
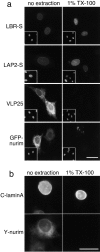
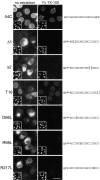
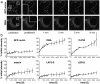
The nuclear envelope (NE) is a distinct subdomain of the ER, but few membrane components have been described that are specific to it. We performed a visual screen in tissue culture cells to identify proteins targeted to the NE. This approach does not require assumptions about the nature of the association with the NE or the physical separation of NE and ER. We confirmed that screening a library of fusions to the green fluorescent protein can be used to identify proteins targeted to various subcompartments of mammalian cells, including the NE. With this approach, we identified a new NE membrane protein, named nurim. Nurim is a multispanning membrane protein without large hydrophilic domains that is very tightly associated with the nucleus. Unlike the known NE membrane proteins, it is neither associated with nuclear pores, nor targeted like lamin-associated membrane proteins. Thus, nurim is a new type of NE membrane protein that is localized to the NE by a distinct mechanism.
Figures
References
-
- Bastos R., Panté N., Burke B. Nuclear pore complex proteins. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1995;162B:257–302. - PubMed
-
- Bione S., Maestrini E., Rivella S., Mancini M., Regis S., Romeo G., Toniolo D. Identification of a novel X-linked gene responsible for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nat. Genet. 1994;8:323–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

