GBF1: A novel Golgi-associated BFA-resistant guanine nucleotide exchange factor that displays specificity for ADP-ribosylation factor 5
- PMID: 10402461
- PMCID: PMC2199737
GBF1: A novel Golgi-associated BFA-resistant guanine nucleotide exchange factor that displays specificity for ADP-ribosylation factor 5
Abstract
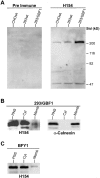
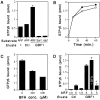
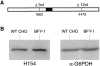
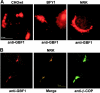
Expression cloning from a cDNA library prepared from a mutant CHO cell line with Golgi-specific resistance to Brefeldin A (BFA) identified a novel 206-kD protein with a Sec7 domain termed GBF1 for Golgi BFA resistance factor 1. Overexpression of GBF1 allowed transfected cells to maintain normal Golgi morphology and grow in the presence of BFA. Golgi- enriched membrane fractions from such transfected cells displayed normal levels of ADP ribosylation factors (ARFs) activation and coat protein recruitment that were, however, BFA resistant. Hexahistidine-tagged-GBF1 exhibited BFA-resistant guanine nucleotide exchange activity that appears specific towards ARF5 at physiological Mg2+concentration. Characterization of cDNAs recovered from the mutant and wild-type parental lines established that transcripts in these cells had identical sequence and, therefore, that GBF1 was naturally BFA resistant. GBF1 was primarily cytosolic but a significant pool colocalized to a perinuclear structure with the beta-subunit of COPI. Immunogold labeling showed highest density of GBF1 over Golgi cisternae and significant labeling over pleiomorphic smooth vesiculotubular structures. The BFA-resistant nature of GBF1 suggests involvement in retrograde traffic.
Figures





References
-
- Achstetter T., Franzusoff A., Field C., Schekman R. SEC7 encodes an unusual, high molecular weight protein required for membrane traffic from the yeast Golgi apparatus. J. Biol. Chem. 1988;263:11711–11717. - PubMed
-
- Antonny B., Beraud-Dufour S., Chardin P., Chabre M. N-terminal hydrophobic residues of the G-protein ADP-ribosylation factor-1 insert into membrane phospholipids upon GDP to GTP exchange. Biochemistry. 1997;36:4675–4684. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F.M., R. Brent, R.E. Kingston, D.D. Moore, J.G. Seidman, J.A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1997. Current Protocols Molecular Biology. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York. 6.21–6.49.
-
- Balch W.E., Rothman J.E. Characterization of protein transport between successive compartments of the Golgi apparatusasymmetric properties of donor and acceptor activities in a cell-free system. Arch Biochem. Biophys. 1985;240:413–425. - PubMed
-
- Balch W.E., Dunphy W.G., Braell W.A., Rothman J.E. Reconstitution of the transport of protein between successive compartments of the Golgi measured by the coupled incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine. Cell. 1984;39:405–416. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
