Yeast homologues of tomosyn and lethal giant larvae function in exocytosis and are associated with the plasma membrane SNARE, Sec9
- PMID: 10402465
- PMCID: PMC2199738
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.146.1.125
Yeast homologues of tomosyn and lethal giant larvae function in exocytosis and are associated with the plasma membrane SNARE, Sec9
Abstract
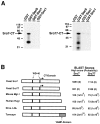
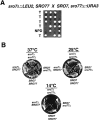
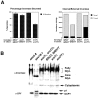
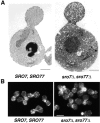
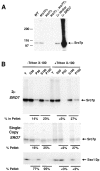
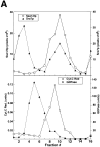
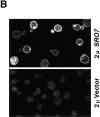
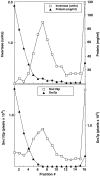
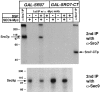
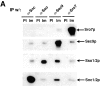
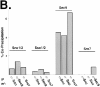
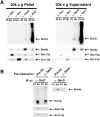
We have identified a pair of related yeast proteins, Sro7p and Sro77p, based on their ability to bind to the plasma membrane SNARE (SNARE) protein, Sec9p. These proteins show significant similarity to the Drosophila tumor suppressor, lethal giant larvae and to the neuronal syntaxin-binding protein, tomosyn. SRO7 and SRO77 have redundant functions as loss of both gene products leads to a severe cold-sensitive growth defect that correlates with a severe defect in exocytosis. We show that similar to Sec9, Sro7/77 functions in the docking and fusion of post-Golgi vesicles with the plasma membrane. In contrast to a previous report, we see no defect in actin polarity under conditions where we see a dramatic effect on secretion. This demonstrates that the primary function of Sro7/77, and likely all members of the lethal giant larvae family, is in exocytosis rather than in regulating the actin cytoskeleton. Analysis of the association of Sro7p and Sec9p demonstrates that Sro7p directly interacts with Sec9p both in the cytosol and in the plasma membrane and can associate with Sec9p in the context of a SNAP receptor complex. Genetic analysis suggests that Sro7 and Sec9 function together in a pathway downstream of the Rho3 GTPase. Taken together, our studies suggest that members of the lethal giant larvae/tomosyn/Sro7 family play an important role in polarized exocytosis by regulating SNARE function on the plasma membrane.
Figures

References
-
- Bartel P., Chien C.T., Sternglanz R., Fields S. Elimination of false positives that arise in using the two-hybrid system. Biotechniques. 1993;14:920–924. - PubMed
-
- Becker D.M., Guarente L. High-efficiency transformation of yeast by electroporation. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:182–187. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

