Myosin light chain kinase functions downstream of Ras/ERK to promote migration of urokinase-type plasminogen activator-stimulated cells in an integrin-selective manner
- PMID: 10402467
- PMCID: PMC2199739
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.146.1.149
Myosin light chain kinase functions downstream of Ras/ERK to promote migration of urokinase-type plasminogen activator-stimulated cells in an integrin-selective manner
Abstract
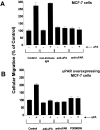
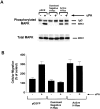
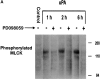
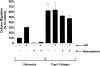
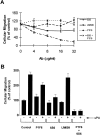
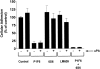
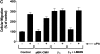
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) activates the mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinases, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1 and 2, in diverse cell types. In this study, we demonstrate that uPA stimulates migration of MCF-7 breast cancer cells, HT 1080 fibrosarcoma cells, and uPAR-overexpressing MCF-7 cells by a mechanism that depends on uPA receptor (uPAR)-ligation and ERK activation. Ras and MAP kinase kinase (MEK) were necessary and sufficient for uPA-induced ERK activation and stimulation of cellular migration, as demonstrated in experiments with dominant-negative and constitutively active mutants of these signaling proteins. Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) was also required for uPA-stimulated cellular migration, as determined in experiments with three separate MLCK inhibitors. When MCF-7 cells were treated with uPA, MLCK was phosphorylated by a MEK-dependent pathway and apparently activated, since serine-phosphorylation of myosin II regulatory light chain (RLC) was also increased. Despite the transient nature of ERK phosphorylation, MLCK remained phosphorylated for at least 6 h. The uPA-induced increase in MCF-7 cell migration was observed selectively on vitronectin-coated surfaces and was mediated by a beta1-integrin (probably alphaVbeta1) and alphaVbeta5. When MCF-7 cells were transfected to express alphaVbeta3 and treated with uPA, ERK was still phosphorylated; however, the cells did not demonstrate increased migration. Neutralizing the function of alphaVbeta3, with blocking antibody, restored the ability of uPA to promote cellular migration. Thus, we have demonstrated that uPA promotes cellular migration, in an integrin-selective manner, by initiating a uPAR-dependent signaling cascade in which Ras, MEK, ERK, and MLCK serve as essential downstream effectors.
Figures






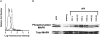
References
-
- Adelstein R.S., Pato M.D., Sellers J.R., de Lanerolle P., Conti M.A. Regulation of contractile proteins by reversible phosphorylation of myosin and myosin kinase. In: Twarog B.M., Levine R.J.C., Dewey M.M., editors. Basic Biology of MusclesA Comparative Approach. Raven Press; New York: 1982. pp. 273–281.
-
- Amano M., Ito M., Kimura K., Fukata Y., Chihara K., Nakano T., Matsuura Y., Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:20246–20249. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen P.A., Kjøller L., Christensen L., Duffy M.J. The urokinase-type plasminogen activator system in cancer metastasisa review. Int. J. Cancer. 1997;72:1–22. - PubMed
-
- Braut-Boucher F., Pichon J., Rat P., Adolphe M., Aubery M., Font J. A non-isotopic, highly sensitive, fluorimetric, cell-cell adhesion microplate assay using calcein AM-labeled lymphocytes. J. Immunol. Methods. 1995;178:41–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

