Drosophila roadblock and Chlamydomonas LC7: a conserved family of dynein-associated proteins involved in axonal transport, flagellar motility, and mitosis
- PMID: 10402468
- PMCID: PMC2199740
Drosophila roadblock and Chlamydomonas LC7: a conserved family of dynein-associated proteins involved in axonal transport, flagellar motility, and mitosis
Abstract
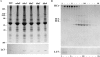
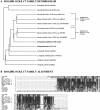
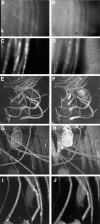
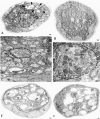
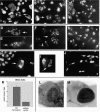
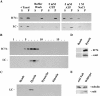
Eukaryotic organisms utilize microtubule-dependent motors of the kinesin and dynein superfamilies to generate intracellular movement. To identify new genes involved in the regulation of axonal transport in Drosophila melanogaster, we undertook a screen based upon the sluggish larval phenotype of known motor mutants. One of the mutants identified in this screen, roadblock (robl), exhibits diverse defects in intracellular transport including axonal transport and mitosis. These defects include intra-axonal accumulations of cargoes, severe axonal degeneration, and aberrant chromosome segregation. The gene identified by robl encodes a 97-amino acid polypeptide that is 57% identical (70% similar) to the 105-amino acid Chlamydomonas outer arm dynein-associated protein LC7, also reported here. Both robl and LC7 have homology to several other genes from fruit fly, nematode, and mammals, but not Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Furthermore, we demonstrate that members of this family of proteins are associated with both flagellar outer arm dynein and Drosophila and rat brain cytoplasmic dynein. We propose that roadblock/LC7 family members may modulate specific dynein functions.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
