Neuropilin-1 mediates collapsin-1/semaphorin III inhibition of endothelial cell motility: functional competition of collapsin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor-165
- PMID: 10402473
- PMCID: PMC2199727
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.146.1.233
Neuropilin-1 mediates collapsin-1/semaphorin III inhibition of endothelial cell motility: functional competition of collapsin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor-165
Abstract
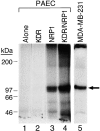
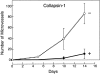
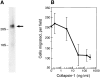
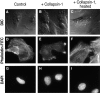
Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) is a receptor for two unrelated ligands with disparate activities, vascular endothelial growth factor-165 (VEGF165), an angiogenesis factor, and semaphorin/collapsins, mediators of neuronal guidance. To determine whether semaphorin/collapsins could interact with NRP1 in nonneuronal cells, the effects of recombinant collapsin-1 on endothelial cells (EC) were examined. Collapsin-1 inhibited the motility of porcine aortic EC (PAEC) expressing NRP1 alone; coexpressing KDR and NRP1 (PAEC/KDR/NRP1), but not parental PAEC; or PAEC expressing KDR alone. The motility of PAEC expressing NRP1 was inhibited by 65-75% and this inhibition was abrogated by anti-NRP1 antibody. In contrast, VEGF165 stimulated the motility of PAEC/KDR/NRP1. When VEGF165 and collapsin-1 were added simultaneously to PAEC/KDR/NRP1, dorsal root ganglia (DRG), and COS-7/NRP1 cells, they competed with each other in EC motility, DRG collapse, and NRP1-binding assays, respectively, suggesting that the two ligands have overlapping NRP1 binding sites. Collapsin-1 rapidly disrupted the formation of lamellipodia and induced depolymerization of F-actin in an NRP1-dependent manner. In an in vitro angiogenesis assay, collapsin-1 inhibited the capillary sprouting of EC from rat aortic ring segments. These results suggest that collapsin-1 can inhibit EC motility as well as axon motility, that these inhibitory effects on motility are mediated by NRP1, and that VEGF165 and collapsin-1 compete for NRP1-binding sites.
Figures




References
-
- Behar O., Golden J.A., Mashimo H., Schoen F.J., Fishman M.C. Semaphorin III is needed for normal patterning and growth of nerves, bones and heart. Nature. 1996;383:525–528. - PubMed
-
- Feiner L., Koppel A.M., Kobayashi H., Raper J.A. Secreted chick semaphorins bind recombinant neuropilin with similar affinities but bind different subsets of neurons in situ. Neuron. 1997;19:539–545. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N., Chen H., Davis-Smyth T., Gerber H.P., Nguyen T.N., Peers D., Chisholm V., Hillan K.J., Schwall R.H. Vascular endothelial growth factor is essential for corpus luteum angiogenesis. Nat. Med. 1998;4:336–340. - PubMed
-
- Fujisawa H., Takagi S., Hirata T. Growth-associated expression of a membrane protein, neuropilin, in Xenopus optic nerve fibers. Dev. Neurosci. 1995;17:343–349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

