Interleukin 1 and interleukin 1beta converting enzyme (caspase 1) expression in the human colonic epithelial barrier. Caspase 1 downregulation in colon cancer
- PMID: 10403737
- PMCID: PMC1727615
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.45.2.246
Interleukin 1 and interleukin 1beta converting enzyme (caspase 1) expression in the human colonic epithelial barrier. Caspase 1 downregulation in colon cancer
Abstract
Background: Interleukin (IL) 1beta converting enzyme (now known as caspase 1) is able to process pro-IL-1beta into its active form and is involved in proapoptotic signalling.
Aims: To characterise IL-1 and caspase 1 expression in human colonic epithelial cells.
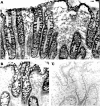
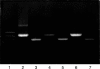
Methods: Intracellular IL-1 content (IL-1alpha and IL-1beta) was measured by ELISA in freshly isolated human normal colonocytes. Caspase 1 expression was determined both at the mRNA level using in situ hybridisation and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, and at the protein level by immunoblotting experiments using antibodies specific for the proform of caspase 1 and for its cleavage forms.
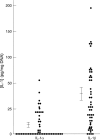
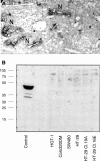
Results: Low amounts of IL-1beta were found in nearly all preparations (92%), and IL-1alpha was detected in only 45% of human colonocyte preparations. The normal colonic epithelium strongly expressed caspase 1, both at the mRNA level and at the protein level in its latent form. In contrast, caspase 1 was not expressed in colon cancer (primary colonic adenocarcinomas and cancer cell lines).
Conclusions: The demonstration that the human colonic epithelial barrier is able to express caspase 1 and its substrate IL-1beta reinforces the concept that, under certain conditions, the epithelium could trigger an inflammatory reaction. In addition, the finding that caspase 1 was downregulated in colonic adenocarcinomas supports the concept that disrupted apoptosis pathways may be involved in tumour formation and/or may confer resistance to treatment.
Figures
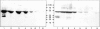
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
