Inducible nitric oxide synthase is expressed in joints of goats in the late stage of infection with caprine arthritis encephalitis virus
- PMID: 10403918
- PMCID: PMC1905485
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00932.x
Inducible nitric oxide synthase is expressed in joints of goats in the late stage of infection with caprine arthritis encephalitis virus
Abstract
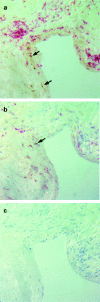
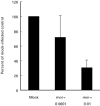
We have studied the expression of the inducible form of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in joints of goats infected with the caprine arthritis encephalitis virus (CAEV). Nitric oxide generated by iNOS is thought to play an important role in the pathogenesis of various types of arthritis, especially rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in humans. Surprisingly, iNOS immunoreactivity was found only in joints of long-term infected goats with severe clinical arthritis, whereas-despite the presence of high numbers of inflammatory cells in the synovial tissue-no iNOS immunoreactivity was detected in mildly arthritic and in short-term experimentally infected goats. Most iNOS-positive cells expressed neither MHC class II nor CD68, which suggests that they were fibroblast-like synoviocytes. In situ hybridization studies showed that there was no correlation between iNOS immunoreactivity and detectable virus expression in the joint. In addition, infection of macrophages in vitro-the major host cells of CAEV in vivo-did not lead to increased iNOS mRNA expression. In response to stimulation, similar levels of iNOS expression were observed in infected and in uninfected macrophages. These findings suggest that the expression of iNOS is a feature of late-stage chronic arthritis and is not involved in the development of the inflammatory lesions. Both the lack of co-localization of iNOS protein and viral transcripts in the joint and the finding that CAEV does not stimulate the expression of iNOS in vitro further suggest that iNOS is not directly induced by the virus or the anti-viral immune response in the joint, that it may well, however, be involved in tissue remodelling or scar formation.
Figures
References
-
- Moncada S, Higgs EA, Hodson HF, et al. The L-arginine–nitric oxide pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1991;17:S1–S9.
-
- MacMicking JD, Nathan C, Hom G, et al. Altered responses to bacterial infection and endotoxic shock in mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase. Cell. 1995;81:641–50. - PubMed
-
- Ueki Y, Miyake S, Tominaga Y, Eguchi K. Increased nitric oxide levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:230–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

