Enhancing of anti-viral activity against HIV-1 by stimulation of CD8+ T cells with thymic peptides
- PMID: 10403919
- PMCID: PMC1905482
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00936.x
Enhancing of anti-viral activity against HIV-1 by stimulation of CD8+ T cells with thymic peptides
Abstract
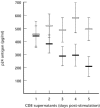
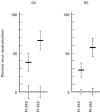
HIV-1 can be neutralized by soluble factors produced and secreted by activated CD8+ T cells. Production of such anti-viral CD8 factors (including chemokines) can be induced with IL-2 or phytohaemagglutinin (PHA). In addition to PHA or IL-2, we have co-stimulated CD8+ T cells with PHA/IL-2 and a mixture of thymic peptides (TP) of molecular weights below 10 kD. For the activation, CD8+ T cells were purified from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of HIV-1- individuals and any resultant anti-viral activity was monitored using an HIV-1 neutralization assay. Using HIV-1 isolates highly resistant to chemokine inhibition we detected significantly higher levels of HIV-1 neutralizing activity in CD8+ T cell culture supernatants which had been co-activated with TP. When the TP-induced anti-viral activity was monitored, neutralization of both non-syncytia-inducing (NSI) and syncytia-inducing (SI) patient isolates was enhanced by 38% (NSI, PHA +/- TP), 66% (SI, PHA +/- TP), 28% (NSI, IL-2 +/- TP), and 57% (SI, IL-2 +/- TP) compared with the anti-viral activity present in supernatants from CD8+ T cell cultures stimulated only with PHA or IL-2. Peptide sequence analysis of purified TP showed that the TP mixture predominantly contains peptides with homology to human histone and collagen sequences. Our data demonstrate that CD8+ T cells are additionally activated by a mixture of TP. In this way, the production of HIV-1 neutralizing CD8 factors can be enhanced.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The CXC chemokine stromal cell-derived factor 1 is not responsible for CD8+ T cell suppression of syncytia-inducing strains of HIV-1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Sep 2;94(18):9842-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.18.9842. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9275213 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous and antigen-induced chemokine production in exposed but uninfected partners of HIV type 1-infected individuals in North India.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2007 Feb;23(2):261-8. doi: 10.1089/aid.2006.0146. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2007. PMID: 17331032
-
Natural killer cells from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected individuals are an important source of CC-chemokines and suppress HIV-1 entry and replication in vitro.J Clin Invest. 1998 Jul 1;102(1):223-31. doi: 10.1172/JCI2323. J Clin Invest. 1998. PMID: 9649576 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-2 reconstitutes defective human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and cytomegalovirus (CMV) specific CD8+ T cell proliferation in HIV infection.J Med Virol. 2006 Sep;78(9):1147-57. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20675. J Med Virol. 2006. PMID: 16847956
-
Modulation of the strength and character of HIV-specific CD8+ T cell responses with heteroclitic peptides.AIDS Res Ther. 2017 Sep 12;14(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12981-017-0170-y. AIDS Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28893274 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Walker CM, Moody DJ, Stites DP, Levy JA. CD8+ lymphocytes can control HIV infection in vitro by suppressing virus replication. Science. 1986;234:1563–6. - PubMed
-
- Walker CM, Moody DJ, Stites DP, Levy JA. CD8+ T lymphocytes control of HIV replication in cultured CD4+ cells varies among infected individuals. Cell Immunol. 1989;119:470–5. - PubMed
-
- Cocchi F, DeVico AL, Garzino-Demo A, Arya SK, Gallo RC, Lusso P. Identification of RANTES, MIP-1 alpha, and MIP-1 beta as the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ T cells. Science. 1995;270:1811–5. - PubMed
-
- Oberlin E, Amara A, Bachelerie F, et al. The CXC chemokine SDF-1 is the ligand for LESTR/fusin and prevents infection by T-cell-line-adapted HIV-1. Nature. 1996;382:833–5. - PubMed
-
- Bleul CC, Farzan M, Choe H, Parolin C, Clark-Lewis I, Sodroski J, Springer TA. The lymphocyte chemoattractant SDF-1 is a ligand for LESTR/fusin and blocks HIV-1 entry. Nature. 1996;382:829–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

