Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)-dependent protection and synthesis of chemoattractants for mononuclear leucocytes caused by IL-12 in the lungs of mice infected with Cryptococcus neoformans
- PMID: 10403924
- PMCID: PMC1905488
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00955.x
Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)-dependent protection and synthesis of chemoattractants for mononuclear leucocytes caused by IL-12 in the lungs of mice infected with Cryptococcus neoformans
Abstract
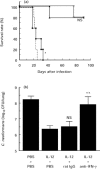
We have recently demonstrated that IL-12 induced cellular inflammatory responses consisting mainly of accumulation of mononuclear leucocytes in the lungs of mice infected with Cryptococcus neoformans and protected mice against fulminant infection. We examined the involvement of endogenously synthesized IFN-gamma in such a response by investigating the effects of a neutralizing monoclonal antibody against this cytokine. The latter treatment completely abrogated the positive effects of IL-12 on survival of infected mice and prevented IL-12-induced elimination of microbials from the lungs. Histopathological examination showed that accumulation of mononuclear leucocytes in the infected lungs caused by IL-12 was clearly inhibited by anti-IFN-gamma MoAb. We also examined the local production of mononuclear cell-attracting chemokines such as monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), regulated upon activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted (RANTES), macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha (MIP-1alpha), MIP-1beta and IFN-gamma-inducible protein 10 (IP-10) in the lungs using a reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method. We found that these chemokines were not synthesized in the infected lungs, while IL-12 treatment markedly induced their production. Interestingly, neutralizing anti-IFN-gamma MoAb strongly suppressed IL-12-induced production of these chemokines. Similar results were obtained with MCP-1 and MIP-1alpha when their synthesis was measured at the protein level using respective ELISA kits. Our results indicate that IFN-gamma plays a central role in the protective effects of IL-12 by inducing mononuclear leucocyte-attracting chemokines and cellular inflammatory responses.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chemokine responses and accumulation of inflammatory cells in the lungs of mice infected with highly virulent Cryptococcus neoformans: effects of interleukin-12.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1999 Sep;25(4):391-402. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.1999.tb01365.x. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10497871
-
Involvement of endogenously synthesized interleukin (IL)-18 in the protective effects of IL-12 against pulmonary infection with Cryptococcus neoformans in mice.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2000 Mar;27(3):191-200. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2000.tb01430.x. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10683463
-
The role of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha/CCL3 in regulation of T cell-mediated immunity to Cryptococcus neoformans infection.J Immunol. 2000 Dec 1;165(11):6429-36. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.11.6429. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11086082
-
Leukocyte recruitment during pulmonary Cryptococcus neoformans infection.Immunopharmacology. 2000 Jul 25;48(3):231-6. doi: 10.1016/s0162-3109(00)00222-8. Immunopharmacology. 2000. PMID: 10960662 Review.
-
Disruption of CCR5 signaling to treat COVID-19-associated cytokine storm: Case series of four critically ill patients treated with leronlimab.J Transl Autoimmun. 2021;4:100083. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100083. Epub 2021 Jan 6. J Transl Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 33521616 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cryptococcal Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome: From Clinical Studies to Animal Experiments.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 7;10(12):2419. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122419. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36557672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-4 receptor-alpha-dependent control of Cryptococcus neoformans in the early phase of pulmonary infection.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 27;9(1):e87341. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087341. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475277 Free PMC article.
-
Adjunctive interferon-γ immunotherapy for the treatment of HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis: a randomized controlled trial.AIDS. 2012 Jun 1;26(9):1105-13. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283536a93. AIDS. 2012. PMID: 22421244 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Resistance and Tolerance to Cryptococcal Infection: An Intricate Balance That Controls the Development of Disease.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 29;10:66. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00066. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30761136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Requirement for CD4(+) T lymphocytes in host resistance against Cryptococcus neoformans in the central nervous system of immunized mice.Infect Immun. 2000 Feb;68(2):456-62. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.2.456-462.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10639404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12: a proinflammatory cytokine with immunoregulatory functions that bridge innate resistance and antigen-specific adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:251–76. - PubMed
-
- Skeen MJ, Ziegler HK. Activation of γδ T cells for production of IFN-γ is mediated by bacteria via macrophage-derived cytokines IL-1 and IL-12. J Immunol. 1995;154:5832–41. - PubMed
-
- Laskay T, Rolinghoff M, Solbach W. Natural killer cells participate in the early defense against Leishmania major infection in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1993;23:2237–41. - PubMed
-
- Rosat JP, MacDonald HR, Louis JA. A role for γδ+ T cells during experimental infection of mice with Leishmania major. J Immunol. 1993;150:550–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

