Depletion of peritoneal CD5+ B cells has no effect on the course of Leishmania major infection in susceptible and resistant mice
- PMID: 10403925
- PMCID: PMC1905474
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00953.x
Depletion of peritoneal CD5+ B cells has no effect on the course of Leishmania major infection in susceptible and resistant mice
Abstract
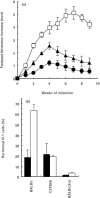
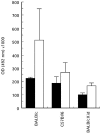
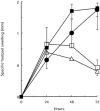
The mouse peritoneal cavity contains a unique self-renewing population of B cells (B-1) derived from fetal liver precursors and mainly producing polyreactive antibodies. Since B-1 cells are a potential source of IL-10, it has been suggested that these cells may contribute to the susceptibility of BALB/c mice to Leishmania major infection by skewing the T helper cell network towards a Th2 phenotype. Accordingly, L. major infection of B cell-defective BALB/c Xid mice (lacking B-1 cells) induces less severe disease compared with controls. However, in addition to the lack of B-1 cells, the Xid immune deficiency is characterized by high endogenous interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production. In the present study, the role of B-1 cells during L. major infection was investigated in mice experimentally depleted of peritoneal B-1 cells. Six weeks old C57Bl/6 and BALB/c mice were lethally irradiated and reconstituted with autologous bone marrow which allows systemic depletion of B-1 cells. Untreated BALB/c, C57Bl/6 as well as BALB/c Xid mice were used as controls. After reconstitution, mice were injected with L. major amastigotes and progression was followed using clinical, parasitological and immunological criteria. As previously reported, BALB/c Xid mice showed a significant reduction in disease progression. In contrast, despite the dramatic reduction of B-1 cells, B-1-depleted BALB/c mice showed similar or even worse disease progression compared with control BALB/c mice. No differences were found between B-1-depleted or control C57Bl/6 mice. Our data suggest that the B-1 cells do not contribute to the susceptibility of BALB/c mice to L. major infection.
Figures
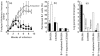
References
-
- Müller I, Garcia-Sanz J, Titus R, Behin R, Louis J. Analysis of the cellular parameters of the immune responses contributing to resistance and susceptibility of mice to infection with the intracellular parasite Leishmania major. Immunol Rev. 1989;112:95–113. - PubMed
-
- Reiner SL, Locksley RM. The regulation of immunity to Leishmania major. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:151–77. - PubMed
-
- Locksley RM, Heinzel FP, Holaday BJ, Reiner SS, Sadick MD. Induction of Th1 and Th2, CD4+ subsets during murine Leishmania major infection. Res Immunol. 1991;142:28–32. - PubMed
-
- Belosevic M, Finbloom DS, Van Der Meide PH. Administration of monoclonal anti-IFN-gamma antibodies in vivo abrogates natural resistance of C3H/HeN mice to infection with Leishmania major. J Immunol. 1989;143:266–74. - PubMed
