Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis spontaneously secrete vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): specific up-regulation by tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in synovial fluid
- PMID: 10403932
- PMCID: PMC1905470
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00949.x
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis spontaneously secrete vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): specific up-regulation by tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in synovial fluid
Abstract
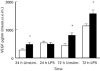
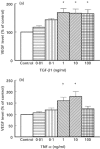
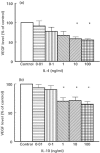
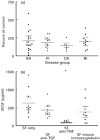
This study was designed to investigate VEGF production from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) compared with healthy controls and to identify the predominant cellular source in PBMC isolated from RA patients. The regulation of PBMC VEGF production by cytokines and synovial fluid (SF) was studied. PBMC were isolated from RA patients and healthy controls and stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), IL-1beta, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, TNF-alpha and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) isoforms for varying time points up to 72 h at 37 degrees C/5% CO2. The effect of SF on VEGF secretion by PBMC was also studied. Supernatant VEGF levels were measured using a flt-1 receptor capture ELISA. RA patients had significantly higher spontaneous production of VEGF compared with controls, and monocytes were identified as the predominant cellular source. RA PBMC VEGF production was up-regulated by TGF-beta isoforms and TNF-alpha and down-regulated by IL-4 and IL-10, with no effect observed with IL-1beta, IL-6 and IL-8. Antibody blocking experiments confirmed that TNF-alpha and not TGF-beta isoforms in SF increased VEGF secretion by RA PBMC. These results emphasize the importance of monocytes as a source of VEGF in the pathophysiology of RA. Several cytokines known to be present in SF can modulate the level of VEGF secretion, but the predominant effect of SF in VEGF up-regulation is shown to be dependent on TNF-alpha.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Placenta growth factor (PlGF) induces vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion from mononuclear cells and is co-expressed with VEGF in synovial fluid.Clin Exp Immunol. 2000 Jan;119(1):182-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01097.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10606981 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of interleukin-18 and its monokine-directed function in rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2001 Mar;40(3):302-9. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.3.302. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2001. PMID: 11285378
-
Heterogeneous requirement of IkappaB kinase 2 for inflammatory cytokine and matrix metalloproteinase production in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for therapy.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Jul;48(7):1901-12. doi: 10.1002/art.11044. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 12847684
-
Recent data on the role for angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis.Joint Bone Spine. 2003 Sep;70(5):321-6. doi: 10.1016/s1297-319x(03)00088-5. Joint Bone Spine. 2003. PMID: 14563458 Review.
-
Interaction(s) between essential fatty acids, eicosanoids, cytokines, growth factors and free radicals: relevance to new therapeutic strategies in rheumatoid arthritis and other collagen vascular diseases.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1991 Dec;44(4):201-10. doi: 10.1016/0952-3278(91)90018-z. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1991. PMID: 1726126 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical Analysis on Quantification and the Inhibitory Effects on Inflammatory Responses from the Fruit of Xanthii fructus.Pharmacogn Mag. 2015 Oct;11(Suppl 4):S585-91. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.172966. Pharmacogn Mag. 2015. PMID: 27013799 Free PMC article.
-
Immune cells regulate VEGF signalling via release of VEGF and antagonistic soluble VEGF receptor-1.Clin Exp Immunol. 2018 Apr;192(1):54-67. doi: 10.1111/cei.13090. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29235095 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve growth factor regulation and production by macrophages in osteoarthritic synovium.Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 Nov;190(2):235-243. doi: 10.1111/cei.13007. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28677145 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF6 inhibits proangiogenic signals in endothelial cells and regulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Mar 2;419(1):66-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.01.128. Epub 2012 Feb 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22326918 Free PMC article.
-
Angiogenesis as a target in rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Nov;62 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):ii60-7. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.suppl_2.ii60. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003. PMID: 14532152 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Harris ED. Rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Eng J Med. 1990;322:1277–88. - PubMed
-
- Janossy G, Panayi G, Duke O, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease of T lymphocyte macrophage immunoregulation. Lancet. 1981;2:834–42. - PubMed
-
- Allen CA, Highton J, Palmer DG. Increased expression of p150.95 and CR3 leukocyte adhesion molecules by mononuclear phagocytes in rheumatoid synovial membranes. Arthritis Rheum. 1989;32:947–54. - PubMed
-
- Kirkham BW, Navaro FJ, Corkill MM, et al. Immunohistochemical localisation of interleukin 1 in rheumatoid and osteoarthritis synovial membrane. J Rheumatol. 1989;28(Suppl.2):47.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

