Field evaluation of the ICT malaria P.f/P.v immunochromatographic test for detection of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax in patients with a presumptive clinical diagnosis of malaria in eastern Indonesia
- PMID: 10405377
- PMCID: PMC85241
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.8.2412-2417.1999
Field evaluation of the ICT malaria P.f/P.v immunochromatographic test for detection of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax in patients with a presumptive clinical diagnosis of malaria in eastern Indonesia
Abstract
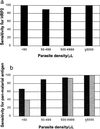
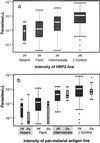
In areas such as eastern Indonesia where both Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax occur, rapid antigen detection tests for malaria need to be able to detect both species. We evaluated the new combined P. falciparum-P. vivax immunochromatographic test (ICT Malaria P.f/P.v.) in Radamata Primary Health Centre, Sumba, Indonesia, from February to May 1998 with 560 symptomatic adults and children with a presumptive clinical diagnosis of malaria. Blinded microscopy was used as the "gold standard," with all discordant and 20% of concordant results cross-checked blindly. Only 50% of those with a presumptive clinical diagnosis of malaria were parasitemic. The ICT Malaria P.f/P.v immunochromatographic test was sensitive (95. 5%) and specific (89.8%) for the diagnosis of falciparum malaria, with a positive predictive value (PPV) and a negative predictive value (NPV) of 88.1 and 96.2%, respectively. HRP2 and panmalarial antigen line intensities were associated with parasitemia density for both species. Although the specificity and NPV for the diagnosis of vivax malaria were 94.8 and 98.2%, respectively, the overall sensitivity (75%) and PPV (50%) for the diagnosis of vivax malaria were less than the desirable levels. The sensitivity for the diagnosis of P. vivax malaria was 96% with parasitemias of >500/microl but only 29% with parasitemias of <500/microl. Nevertheless, compared with the test with HRP2 alone, use of the combined antigen detection test would reduce the rate of undertreatment from 14.7 to 3.6% for microscopy-positive patients, and this would be at the expense of only a modest increase in the rate of overtreatment of microscopy-negative patients from 7.1 to 15. 4%. Cost remains a major obstacle to widespread use in areas of endemicity.
Figures
References
-
- Banchongaksorn T, Prajakwong S, Rooney W, Vickers P. Operational trial of ParaSight-F (dipstick) in the diagnosis of falciparum malaria at the primary health care level. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1997;28:243–246. - PubMed
-
- Bartoloni A, Sabatinelli G, Benucci M. Performance of two rapid tests for Plasmodium falciparum malaria in patients with rheumatoid factors. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1075. - PubMed
-
- Bartoloni A, Strohmeyer M, Sabatinelli G, Benucci M, Serni U, Paradisi F. False positive ParaSight-F test for malaria in patients with rheumatoid factor. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1998;92:33–34. - PubMed
-
- Beadle C, Long G W, Weiss W R, McElroy P D, Maret S M, Oloo A J, Hoffman S L. Diagnosis of malaria by detection of Plasmodium falciparum HRP-2 antigen with a rapid dipstick antigen-capture assay. Lancet. 1994;343:564–568. - PubMed
-
- Caraballo A, Ache A. The evaluation of a dipstick test for Plasmodium falciparum in mining areas of Venezuela. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1996;55:482–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

