Comparison of molecular methods for typing Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- PMID: 10405387
- PMCID: PMC85259
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.8.2473-2478.1999
Comparison of molecular methods for typing Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Abstract
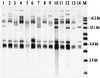
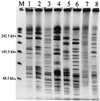
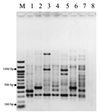
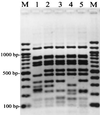
An outbreak of Vibrio parahaemolyticus gastroenteritis on Canada's west coast in 1997 emphasized the need to develop molecular methods for differentiation and typing of these organisms. Isolates were analyzed by enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus sequence (ERIC) PCR, detection of restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP) in rRNA genes (ribotyping), pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), and RFLP analysis of the genetic locus encoding the polar flagellum (Fla locus RFLP analysis). ERIC PCR and ribotyping were the most informative typing methods, especially when used together, while Fla locus RFLP analysis was the least discriminatory. PFGE exhibited good discrimination but suffered from a high incidence of DNA degradation. ERIC PCR and ribotyping will be useful for the evaluation of genetic and epidemiological relationships among V. parahaemolyticus strains.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular typing of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates from the middle-east coastline of China.Int J Food Microbiol. 2012 Feb 15;153(3):402-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.12.001. Epub 2011 Dec 19. Int J Food Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22225982
-
Evaluation of typing of vibrio parahaemolyticus by three PCR methods using specific primers.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Dec;39(12):4233-40. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.12.4233-4240.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11724826 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular typing of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from seafood harvested along the south-west coast of India.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2008 Feb;46(2):198-204. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2007.02304.x. Epub 2007 Dec 20. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18179449
-
The use of genetic typing methods to discriminate among strains of Vibrio cholerae, V. parahaemolyticus, and V. vulnificus.J AOAC Int. 2010 Sep-Oct;93(5):1553-69. J AOAC Int. 2010. PMID: 21140669 Review.
-
[Homology analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated by MPN method using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and automated ribotyping].Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2010 May;39(3):374-80. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2010. PMID: 20568474 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Genotypic analyses of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and development of a pandemic group-specific multiplex PCR assay.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Oct;41(10):4676-82. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.10.4676-4682.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14532202 Free PMC article.
-
Improved isolation and detection of toxigenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus from coastal water in Saudi Arabia using immunomagnetic enrichment.PeerJ. 2021 Oct 29;9:e12402. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12402. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34760388 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism assay for the epidemiological analysis of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Nov;42(11):5205-13. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.11.5205-5213.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15528716 Free PMC article.
-
Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis in differentiation of erysipelothrix species strains.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Nov;39(11):4032-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.11.4032-4036.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11682526 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli isolates associated with nosocomial infections in dogs.J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Oct;40(10):3586-95. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.10.3586-3595.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12354850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blake P A, Weaver R E, Hollis D G. Diseases of humans (other than cholera) caused by vibrios. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:341–367. - PubMed
-
- Dalsgaard A, Serichantalergs O, Echeverria P. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP) of cholera toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae O139 recovered from patients in Thailand, India and Bangladesh. Scand J Infect Dis. 1995;27:585–588. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

