Detection of phylogenetically diverse human immunodeficiency virus type 1 groups M and O from plasma by using highly sensitive and specific generic primers
- PMID: 10405405
- PMCID: PMC85288
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.8.2581-2586.1999
Detection of phylogenetically diverse human immunodeficiency virus type 1 groups M and O from plasma by using highly sensitive and specific generic primers
Abstract
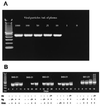
The high degree of genetic diversity within human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), which includes two major groups, M (major) and O (outlier), and various env subtypes within group M (subtypes A to J), has made designing assays that will detect all known HIV-1 strains difficult. We have developed a generic primer set based on the conserved immunodominant region of transmembrane protein gp41 that can reliably amplify as few as 10 copies/PCR of viral DNA from near-full-length clones representing group M subtypes A to H (subtypes I and J were not available). The assay is highly sensitive in detecting plasma viral RNA from HIV-1 strains of diverse geographic origins representing different subtypes of HIV-1 group M as well as HIV-1 group O. Of the 253 group M plasma specimens (subtypes A, 68 specimens; B, 71; C, 19; D, 27; E, 23; F, 33; and G, 12), 250 (98.8%) were amplified by using the gp41 M/O primer set. More importantly, all 32 (100%) group O plasma samples were also amplified with these primers. In vitro spiking experiments further revealed that the assay could reliably detect as few as 25 copies/ml of viral RNA and gave positive signals in HIV-1-seropositive specimens with plasma copy numbers below the limits of detection by all commercially available viral load assays. In addition, analysis of five seroconversion panels indicated that the assay is highly sensitive for early detection of plasma viremia during the "window period." Thus, the highly sensitive assay will be useful for early detection of HIV-1 in clinical specimens from all known HIV-1 infections, regardless of their genotypes and geographic origins.
Figures

References
-
- Alaeus A, Lidman K, Sönnerborg A, Albert J. Subtype-specific problems with quantification of plasma HIV-1 RNA. AIDS. 1997;11:859–865. - PubMed
-
- Apetrei C, Loussert-Ajaka I, Descamps D, Damond F, Saragosti S, Brun-Vezinet F, Simon F. Lack of screening test sensitivity during HIV-1 non-subtype B seroconversions. AIDS. 1996;10:F57–F60. - PubMed
-
- Cavert W. In vitro detection and quantitation of HIV in blood and tissues. AIDS. 1998;12(Suppl. A):S27–S34. - PubMed
-
- Eberle J, Loussert-Ajaka I, Brust S, Zekeng L, Hauser P H, Kaptue L, Knapp S, Damond F, Saragosti S, Simon F, Gürtler L G. Diversity of the immunodominant epitope of gp41 of HIV-1 subtype O and its validity for antibody detection. J Virol Methods. 1997;67:85–91. - PubMed
-
- Felsenstein J. PHYLIP—phylogeny inference package (version 3.2) Cladistics. 1989;5:164–166.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

