Disseminated zygomycosis due to Rhizopus schipperae after heatstroke
- PMID: 10405417
- PMCID: PMC85306
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.8.2656-2662.1999
Disseminated zygomycosis due to Rhizopus schipperae after heatstroke
Abstract
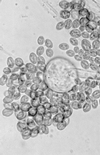
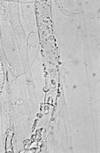
A 21-year-old woman suffered heatstroke and developed diarrhea while trekking across south Texas. The heatstroke was complicated by seizures, rhabdomyolysis, pneumonia, renal failure, and disseminated intravascular coagulation. The patient's stool and blood cultures grew Campylobacter jejuni. The patient subsequently developed paranasal and gastrointestinal zygomycosis and required surgical debridement and a prolonged course of amphotericin B. The zygomycete cultured was Rhizopus schipperae. This is only the second isolate of R. schipperae that has been described. R. schipperae is characterized by the production of clusters of up to 10 sporangiophores arising from simple but well-developed rhizoids. These asexual reproductive propagules are produced on Czapek Dox agar but are absent on routine mycology media, where only chlamydospores are observed. Despite multiorgan failure, bacteremia, and disseminated zygomycosis, the patient survived and had a good neurological outcome. Heatstroke has not been previously described as a risk factor for the development of disseminated zygomycosis.
Figures
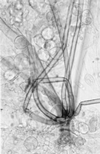
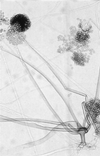
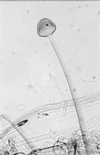
References
-
- Allos B M, Blaser M J. Campylobacter jejuni and the expanding spectrum of related infections. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:1092–1101. - PubMed
-
- Anim J T, Baraka M E, Al-Gamdi S, Sohaibani M O. Morphological alterations in the nasal mucosa in heat stroke. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 1988;8:39–47. - PubMed
-
- Bouchama A. Heatstroke: a new look at an ancient disease. Intensive Care Med. 1995;21:623–625. - PubMed
-
- Bouchama A, el Hussein K, Adra C, Rezeig M, al Shail E, al Sedairy S. Distribution of peripheral blood leukocytes in acute heatstroke. J Appl Physiol. 1992;73:405–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

