Three GABA receptor-mediated postsynaptic potentials in interneurons in the rat lateral geniculate nucleus
- PMID: 10407013
- PMCID: PMC6783068
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-14-05721.1999
Three GABA receptor-mediated postsynaptic potentials in interneurons in the rat lateral geniculate nucleus
Abstract
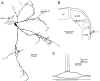
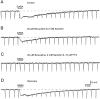
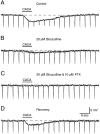
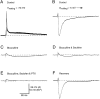
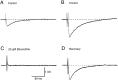
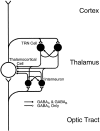
Inhibition is crucial for the thalamus to relay sensory information from the periphery to the cortex and to participate in thalamocortical oscillations. However, the properties of inhibitory synaptic events in interneurons are poorly defined because in part of the technical difficulty of obtaining stable recording from these small cells. With the whole-cell recording technique, we obtained stable recordings from local interneurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus and studied their inhibitory synaptic properties. We found that interneurons expressed three different types of GABA receptors: bicuculline-sensitive GABA(A) receptors, bicuculline-insensitive GABA(A) receptors, and GABA(B) receptors. The reversal potentials of GABA responses were estimated by polarizing the membrane potential. The GABA(A) receptor-mediated responses had a reversal potential of approximately -82 mV, consistent with mediation via Cl(-) channels. The reversal potential for the GABA(B) response was -97 mV, consistent with it being a K(+) conductance. The roles of these GABA receptors in postsynaptic responses were also examined in interneurons. Optic tract stimulation evoked a disynaptic IPSP that was mediated by all three types of GABA receptors and depended on activation of geniculate interneurons. Stimulation of the thalamic reticular nucleus evoked an IPSP, which appeared to be mediated exclusively by bicuculline-sensitive GABA(A) receptors and depended on the activation of reticular cells. The results indicate that geniculate interneurons form a complex neuronal circuitry with thalamocortical and reticular cells via feed-forward and feedback circuits, suggesting that they play a more important role in thalamic function than thought previously.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Somatostatin inhibits GABAergic transmission in the sensory thalamus via presynaptic receptors.Neuroscience. 2000;98(3):513-22. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(00)00107-x. Neuroscience. 2000. PMID: 10869845
-
Dynamic properties of corticothalamic excitatory postsynaptic potentials and thalamic reticular inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in thalamocortical neurons of the guinea-pig dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus.Neuroscience. 1999;91(1):7-20. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00557-0. Neuroscience. 1999. PMID: 10336055
-
On the properties and origin of the GABAB inhibitory postsynaptic potential recorded in morphologically identified projection cells of the cat dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus.Neuroscience. 1989;33(1):23-33. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90307-2. Neuroscience. 1989. PMID: 2557560
-
Activation of presynaptic GABAB receptors modulates GABAergic and glutamatergic inputs to the medial geniculate body.Hear Res. 2011 Oct;280(1-2):157-65. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2011.05.018. Epub 2011 May 31. Hear Res. 2011. PMID: 21664264
-
Regulation of excitability by extrasynaptic GABA(A) receptors.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2008;44:29-48. doi: 10.1007/400_2007_030. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2008. PMID: 17671772 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for inhibition mediated by coassembly of GABAA and GABAC receptor subunits in native central neurons.J Neurosci. 2004 Aug 18;24(33):7241-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1979-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15317850 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent inhibitory circuitry in the deep layers of the rabbit superior colliculus.J Physiol. 2000 Mar 15;523 Pt 3(Pt 3):731-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00731.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10718751 Free PMC article.
-
Postnatal development of GABAergic signalling in the rat lateral geniculate nucleus: presynaptic dendritic mechanisms.J Physiol. 2003 Jan 1;546(Pt 1):137-48. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.030643. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12509484 Free PMC article.
-
Simple synaptic modulations implement diverse novelty computations.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 27:2023.08.16.553635. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.16.553635. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep. 2024 May 28;43(5):114188. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114188. PMID: 37645978 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
An Update on GABAρ Receptors.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2010 Dec;8(4):422-33. doi: 10.2174/157015910793358141. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2010. PMID: 21629448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlsén G, Lindström S, Lo F-S. Interaction between inhibitory pathway to principal cells in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1985;58:134–143. - PubMed
-
- Akaike N, Hattori K, Oomura Y, Carpenter DO. Bicuculline and picrotoxin block gamma-aminobutyric acid-gated Cl− conductance by different mechanisms. Experientia. 1985;41:70–71. - PubMed
-
- Blanton MG, LoTurco TJ, Kriegstein AR. Whole cell recording from neurons in slices of reptilian and mammalian cerebral cortex. J Neurosci Methods. 1989;30:203–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
