Targeted mutagenesis of the POU-domain gene Brn4/Pou3f4 causes developmental defects in the inner ear
- PMID: 10407036
- PMCID: PMC6783103
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-14-05980.1999
Targeted mutagenesis of the POU-domain gene Brn4/Pou3f4 causes developmental defects in the inner ear
Abstract
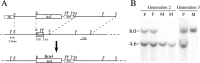
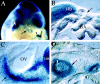
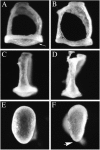
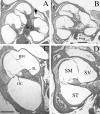
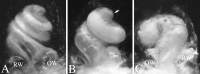
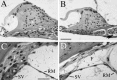
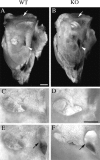
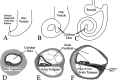
Targeted mutagenesis in mice demonstrates that the POU-domain gene Brn4/Pou3f4 plays a crucial role in the patterning of the mesenchymal compartment of the inner ear. Brn4 is expressed extensively throughout the condensing mesenchyme of the developing inner ear. Mutant animals displayed behavioral anomalies that resulted from functional deficits in both the auditory and vestibular systems, including vertical head bobbing, changes in gait, and hearing loss. Anatomical analyses of the temporal bone, which is derived in part from the otic mesenchyme, demonstrated several dysplastic features in the mutant animals, including enlargement of the internal auditory meatus. Many phenotypic features of the mutant animals resulted from the reduction or thinning of the bony compartment of the inner ear. Histological analyses demonstrated a hypoplasia of those regions of the cochlea derived from otic mesenchyme, including the spiral limbus, the scala tympani, and strial fibrocytes. Interestingly, we observed a reduction in the coiling of the cochlea, which suggests that Brn-4 plays a role in the epithelial-mesenchymal communication necessary for the cochlear anlage to develop correctly. Finally, the stapes demonstrated several malformations, including changes in the size and morphology of its footplate. Because the stapes anlage does not express the Brn4 gene, stapes malformations suggest that the Brn4 gene also plays a role in mesenchymal-mesenchymal signaling. On the basis of these data, we suggest that Brn-4 enhances the survival of mesodermal cells during the mesenchymal remodeling that forms the mature bony labyrinth and regulates inductive signaling mechanisms in the otic mesenchyme.
Figures


References
-
- Alvarez-Bolado G, Rosenfeld MG, Swanson LW. Model of forebrain regionalization based on spatiotemporal patterns of POU-III homeobox gene expression, birthdates, and morphological features. J Comp Neurol. 1995;355:237–295. - PubMed
-
- Bermingham JR, Scherer SS, O’Connell S, Arroyo E, Kalla KA, Powell FL, Rosenfeld MG. Tst-1/Oct-6/SCIP regulates a unique step in peripheral myelination and is required for normal respiration. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1751–1762. - PubMed
-
- Curthoys IS. Scarpa’s ganglion in the rat and guinea pig. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 1981;92:107–113. - PubMed
-
- de Kok YJ, Merkx GF, van der Maarel SM, Huber I, Malcolm S, Ropers HH, Cremers FP. A duplication/paracentric inversion associated with familial X-linked deafness (DFN3) suggests the presence of a regulatory element more than 400 kb upstream of the POU3F4 gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1995a;4:2145–2150. - PubMed
-
- de Kok YJ, van der Maarel SM, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Huber I, Monaco AP, Malcolm S, Pembrey ME, Ropers HH, Cremers FP. Association between X-linked mixed deafness and mutations in the POU domain gene POU3F4. Science. 1995b;267:685–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
