Risk stratification after acute myocardial infarction by Doppler stroke distance measurement
- PMID: 10409534
- PMCID: PMC1729154
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.82.2.187
Risk stratification after acute myocardial infarction by Doppler stroke distance measurement
Abstract
Objective: To establish the value of Doppler stroke distance measurement as a predictor of mortality risk following acute myocardial infarction.
Design: Follow up study.
Setting: Coronary care unit of a teaching and district general hospital.
Subjects: 378 patients (mean age 61 years) with acute myocardial infarction followed up for a mean of five years (range 2-7 years); 299 (79%) patients received thrombolysis.
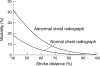
Main outcome measures: Stroke distance (the systolic velocity integral of blood flow in the aortic arch (percentage of age predicted normal value)); presence or absence of left ventricular failure on the admission chest radiograph; the codified admission ECG; death during follow up.
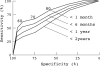
Results: Mean (SD) stroke distance was 81 (19)% and five year survival 76%. For patients with stroke distance > 100% (n = 60), 82-100% (n = 134), 63-81% (n = 122), and < 63% (n = 62), the one month mortality rates were 0%, 1.5%, 4%, and 18%, respectively; the corresponding estimates for mortality at five years were 17%, 19%, 24%, and 43%. Survival was independently related to age (p < 0.0001), stroke distance (p < 0.0001), and chest radiograph appearance (p = 0.002), but not to ECG codes (p = 0.31) or receipt of thrombolysis (p = 0.60). The areas under receiver operator characteristic plots for stroke distance measurements were 82%, 76%, 71%, and 65% for deaths within one month, six months, one year, and two years, respectively.
Conclusions: The bedside measurement of stroke distance stratifies mortality risk after acute myocardial infarction. The predictive ability of this simple measure of left ventricular systolic function compares well with published accounts of the more complex measurement of ejection fraction.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Atrial filling fraction predicts left ventricular systolic function after myocardial infarction: pre-discharge echocardiographic evaluation].Cardiologia. 1995 Oct;40(10):763-8. Cardiologia. 1995. PMID: 8819737 Italian.
-
Strain echocardiography improves risk prediction of ventricular arrhythmias after myocardial infarction.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013 Aug;6(8):841-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.03.005. Epub 2013 Jul 10. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23850251
-
Usefulness of two-dimensional longitudinal strain pattern to predict left ventricular recovery and in-hospital complications after acute anterior myocardial infarction treated successfully by primary angioplasty.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015 Nov;28(11):1366-75. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2015.07.022. Epub 2015 Sep 1. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015. PMID: 26341122 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
-
Short early filling deceleration time on day 1 after acute myocardial infarction is associated with short and long term left ventricular remodelling.Heart. 2001 May;85(5):527-32. doi: 10.1136/heart.85.5.527. Heart. 2001. PMID: 11303004 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Left ventricular outflow tract velocity time integral outperforms ejection fraction and Doppler-derived cardiac output for predicting outcomes in a select advanced heart failure cohort.Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2017 Jul 3;15(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12947-017-0109-4. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2017. PMID: 28673293 Free PMC article.
-
Time-Velocity Integral of Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Predicts Worse Long-Term Survival in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.JACC Asia. 2022 May 17;2(3):235-243. doi: 10.1016/j.jacasi.2022.02.002. eCollection 2022 Jun. JACC Asia. 2022. PMID: 36338398 Free PMC article.
-
LVOT-VTI is a Useful Indicator of Low Ventricular Function in Young Patients.Pediatr Cardiol. 2017 Aug;38(6):1148-1154. doi: 10.1007/s00246-017-1630-9. Epub 2017 May 22. Pediatr Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28534242
-
Left ventricular outflow tract velocity time integral in hospitalized heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.ESC Heart Fail. 2020 Feb;7(1):167-175. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12541. Epub 2019 Dec 18. ESC Heart Fail. 2020. PMID: 31851433 Free PMC article.
-
A combination of left ventricular outflow tract velocity time integral and lung ultrasound to predict mortality in ST elevation myocardial infarction.Intern Emerg Med. 2024 Nov;19(8):2167-2176. doi: 10.1007/s11739-024-03719-z. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Intern Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 39044051
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
