Dual signaling role of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 in regulating expression of acute-phase plasma proteins by interleukin-6 cytokine receptors in hepatic cells
- PMID: 10409724
- PMCID: PMC84376
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.8.5326
Dual signaling role of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 in regulating expression of acute-phase plasma proteins by interleukin-6 cytokine receptors in hepatic cells
Abstract
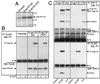
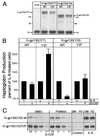
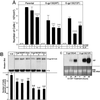
One of the major actions of interleukin-6 (IL-6) is the transcriptional activation of acute-phase plasma proteins (APP) genes in liver cells. Signaling by the IL-6 receptor is mediated through the signal transducing subunit gp130 and involves the activation of Janus-associated kinases (JAKs), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), and mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase. Functional analysis of gp130 in rat hepatoma cells by using transduced chimeric G-CSFR-gp130 receptor constructs demonstrates that SHP-2, the Src homology 2 (SH2) domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase, acts as a negative regulator of the JAK/STAT signaling in part by downregulating JAK activity, thereby indirectly moderating the induction of STAT3-dependent APP genes. This study shows that in hepatoma cells, the recruitment and tyrosine phosphorylation of SHP-2, but not SHC, is the primary signaling event associated with the activation of MAP kinases (ERK1/2) by gp130. Overexpression of truncated SHP-2 that lacks Grb2-interacting sites, but not the full-length catalytically inactive SHP-2, reduces ERK activation by IL-6, confirming the signal-mediating role of SHP-2. Activation of ERK1/2 is correlated with induction of the immediate-early response genes. Stimulation of the c-fos, c-jun, and egr-1 genes is essentially absent in cells expressing gp130 with a Y759F mutation, which is unable to recruit SHP-2. Interestingly, both JAK/STAT and SHP-2 pathways regulate the induction of the junB gene. Moreover, disengagement of SHP-2 from gp130 signaling not only enhances APP gene induction but also further reduces cell proliferation, in part correlated with the attenuated expression of immediate-early response genes. These results suggest that IL-6 regulation of APP genes is affected by SHP-2 in two ways: SHP-2 acts as a phosphatase on the JAK/STAT pathway and serves as linker to the MAP kinase pathway, which in turn moderates APP production.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Activation of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 via the interleukin-6 signal transducing receptor protein gp130 requires tyrosine kinase Jak1 and limits acute-phase protein expression.Biochem J. 1998 Nov 1;335 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):557-65. doi: 10.1042/bj3350557. Biochem J. 1998. PMID: 9794795 Free PMC article.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 2 (SHP-2) moderates signaling by gp130 but is not required for the induction of acute-phase plasma protein genes in hepatic cells.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Mar;18(3):1525-33. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.3.1525. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9488469 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-alpha induces tyrosine phosphorylation and recruitment of the Src homology protein-tyrosine phosphatase 2 to the gp130 signal-transducing subunit of the IL-6 receptor complex.J Immunol. 2003 Jul 1;171(1):257-66. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.1.257. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12817006
-
Interleukin-6, CD45 and the src-kinases in myeloma cell proliferation.Leuk Lymphoma. 2003 Sep;44(9):1477-81. doi: 10.3109/10428190309178767. Leuk Lymphoma. 2003. PMID: 14565647 Review.
-
Interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway.Biochem J. 1998 Sep 1;334 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):297-314. doi: 10.1042/bj3340297. Biochem J. 1998. PMID: 9716487 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intrathecal delivery of IL-6 reactivates the intrinsic growth capacity of pyramidal cells in the sensorimotor cortex after spinal cord injury.PLoS One. 2015 May 19;10(5):e0127772. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127772. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25992975 Free PMC article.
-
Growth Factors, and Cytokines; Understanding the Role of Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP2 in Gametogenesis and Early Embryo Development.Cells. 2020 Jul 29;9(8):1798. doi: 10.3390/cells9081798. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32751109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-talk between interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta) and IL-6 signalling pathways: IL-1beta selectively inhibits IL-6-activated signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 1 (STAT1) by a proteasome-dependent mechanism.Biochem J. 2000 Dec 15;352 Pt 3(Pt 3):913-9. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 11104703 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term infusion of interleukin-6 does not induce insulin resistance in vivo or impair insulin signalling in rats.Diabetologia. 2004 Nov;47(11):1879-87. doi: 10.1007/s00125-004-1544-y. Epub 2004 Nov 17. Diabetologia. 2004. PMID: 15551046
-
Regulation of Jak2 through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway involves phosphorylation of Jak2 on Y1007 and interaction with SOCS-1.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 May;22(10):3316-26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.10.3316-3326.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11971965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi M, Ishino M, Torigoe T, Minami Y, Matozaki T, Miyazaki T, Taniguchi T, Hinoda Y, Imai K. Interleukin-2 induces tyrosine phosphorylation of SHP-2 through IL-2 receptor beta chain. Oncogene. 1997;14:1629–1633. - PubMed
-
- Auble D T, Brinckerhoff C E. The AP-1 sequence is necessary but not sufficient for phorbol induction of collagenase in fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1991;30:4629–4635. - PubMed
-
- Baumann H, Prowse K R, Marinokovic S, Won K-A, Jahreis G P. Stimulation of hepatic acute phase response by cytokines and glucocorticoids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;557:280–295. - PubMed
-
- Baumann H, Gearing D, Ziegler S F. Signaling by the cytoplasmic domain of hematopoietin receptors involves two distinguishable mechanisms in hepatic cells. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:16297–16304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
