Notch and wingless regulate expression of cuticle patterning genes
- PMID: 10409762
- PMCID: PMC84425
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.8.5743
Notch and wingless regulate expression of cuticle patterning genes
Abstract
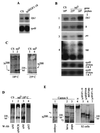
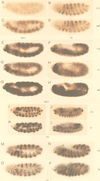
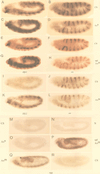
The cell surface receptor Notch is required during Drosophila embryogenesis for production of epidermal precursor cells. The secreted factor Wingless is required for specifying different types of cells during differentiation of tissues from these epidermal precursor cells. The results reported here show that the full-length Notch and a form of Notch truncated in the amino terminus associate with Wingless in S2 cells and in embryos. In S2 cells, Wingless and the two different forms of Notch regulate expression of Dfrizzled 2, a receptor of Wg; hairy, a negative regulator of achaete expression; shaggy, a negative regulator of engrailed expression; and patched, a negative regulator of wingless expression. Analyses of expression of the same genes in mutant N embryos indicate that the pattern of gene regulations observed in vitro reflects regulations in vivo. These results suggest that the strong genetic interactions observed between Notch and wingless genes during development of Drosophila is at least partly due to regulation of expression of cuticle patterning genes by Wingless and the two forms of Notch.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Frizzled and Dfrizzled-2 function as redundant receptors for Wingless during Drosophila embryonic development.Development. 1999 Sep;126(18):4175-86. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.18.4175. Development. 1999. PMID: 10457026
-
Use of dsRNA-mediated genetic interference to demonstrate that frizzled and frizzled 2 act in the wingless pathway.Cell. 1998 Dec 23;95(7):1017-26. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81725-0. Cell. 1998. PMID: 9875855
-
Drosophila ciD encodes a hybrid Pangolin/Cubitus interruptus protein that diverts the Wingless into the Hedgehog signaling pathway.Mech Dev. 1998 Nov;78(1-2):141-51. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(98)00163-4. Mech Dev. 1998. PMID: 9858713
-
Cell patterning in the Drosophila segment: engrailed and wingless antigen distributions in segment polarity mutant embryos.Dev Suppl. 1993:105-14. Dev Suppl. 1993. PMID: 8049466 Review.
-
Serpentine proteins slither into the wingless and hedgehog fields.Cell. 1996 Aug 23;86(4):513-6. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80124-5. Cell. 1996. PMID: 8752205 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Notch signaling in mammary development and oncogenesis.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2004 Apr;9(2):145-63. doi: 10.1023/B:JOMG.0000037159.63644.81. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2004. PMID: 15300010 Review.
-
Regulation of Notch signaling by Drosophila heparan sulfate 3-O sulfotransferase.J Cell Biol. 2004 Sep 27;166(7):1069-79. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200403077. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15452147 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the expression of the Alzheimer’s disease-associated presenilin gene in drosophila heart leads to cardiac dysfunction.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2011 May;8(3):313-22. doi: 10.2174/156720511795563746. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2011. PMID: 21524270 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt-Notch signalling crosstalk in development and disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Sep;71(18):3553-67. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1644-x. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24942883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The notch intracellular domain can function as a coactivator for LEF-1.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Nov;21(22):7537-44. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.22.7537-7544.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11604490 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alton A K, Fechtel K, Kopczynski C C, Shepard S B, Kooh P J, Muskavitch M A T. Molecular genetics of Delta, a locus required for ectodermal differentiation in Drosophila. Dev Genet. 1989;10:261–272. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Matsuno K, Fortini M E. Notch signaling. Science. 1995;268:225–232. - PubMed
-
- Axelrod J D, Matsuno K, Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Perrimon N. Interaction between Wingless and Notch signaling pathways mediated by Dishevelled. Science. 1996;271:1826–1832. - PubMed
-
- Baker N E, Mlodzik M, Rubin G M. Spacing differentiation in the developing Drosophila eye: a fibrinogen-related lateral inhibitor encoded by scabrous. Science. 1990;250:1370–1377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
