Akt/Protein kinase B inhibits cell death by preventing the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria
- PMID: 10409766
- PMCID: PMC84429
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.8.5800
Akt/Protein kinase B inhibits cell death by preventing the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria
Abstract
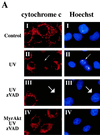
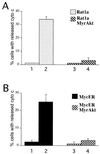
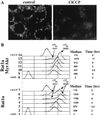
Growth factors signaling through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway promote cell survival. The mechanism by which the serine/threonine kinase Akt prevents cell death remains unclear. We have previously shown that Akt inhibits the activity of DEVD-targeted caspases without changing the steady-state levels of Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L). Here we show that Akt inhibits apoptosis and the processing of procaspases to their active forms by delaying mitochondrial changes in a caspase-independent manner. Akt activation is sufficient to inhibit the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria and the alterations in the inner mitochondrial membrane potential. However, Akt cannot inhibit apoptosis induced by microinjection of cytochrome c. We also demonstrated that Akt inhibits apoptosis and cytochrome c release induced by several proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members. Taken together, our results show that Akt promotes cell survival by intervening in the apoptosis cascade before cytochrome c release and caspase activation via a mechanism that is distinct from Bad phosphorylation.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Akt regulates cell survival and apoptosis at a postmitochondrial level.J Cell Biol. 2000 Oct 30;151(3):483-94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.3.483. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11062251 Free PMC article.
-
C5b-9 terminal complement complex protects oligodendrocytes from death by regulating Bad through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway.J Immunol. 2001 Aug 15;167(4):2305-11. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.4.2305. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11490019
-
cAMP inhibits bile acid-induced apoptosis by blocking caspase activation and cytochrome c release.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002 Sep;283(3):G727-38. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00410.2001. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12181189
-
Mechanisms of cytochrome c release by proapoptotic BCL-2 family members.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 May 9;304(3):437-44. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)00615-6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003. PMID: 12729577 Review.
-
Cellular survival: a play in three Akts.Genes Dev. 1999 Nov 15;13(22):2905-27. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.22.2905. Genes Dev. 1999. PMID: 10579998 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Expression of phosphorylated mTOR and its regulatory protein is related to biological behaviors of ameloblastoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(7):660-7. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22977662 Free PMC article.
-
Securidaca-saponins are natural inhibitors of AKT, MCL-1, and BCL2L1 in cervical cancer cells.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Nov 15;10:5709-5724. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S163328. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30532593 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase-independent photoreceptor apoptosis in mouse models of retinal degeneration.J Neurosci. 2003 Jul 2;23(13):5723-31. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-13-05723.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12843276 Free PMC article.
-
Strictinin, a novel ROR1-inhibitor, represses triple negative breast cancer survival and migration via modulation of PI3K/AKT/GSK3ß activity.PLoS One. 2019 May 31;14(5):e0217789. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217789. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31150511 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of berberine against neurodegenerative diseases.Sci China Life Sci. 2015 Jun;58(6):564-9. doi: 10.1007/s11427-015-4829-0. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Sci China Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25749423 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams J M, Cory S. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 1998;281:1322–1326. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann A, Agapite J, McCall K, Steller H. The Drosophila gene hid is a direct molecular target of Ras-dependent survival signaling. Cell. 1998;95:331–341. - PubMed
-
- Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond M J, Lin M Z, Juo P, Hu L S, Anderson M J, Arden K C, Blenis J, Greenberg M E. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell. 1999;96:857–868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
