Multiple roles of ligand in transforming the dioxin receptor to an active basic helix-loop-helix/PAS transcription factor complex with the nuclear protein Arnt
- PMID: 10409767
- PMCID: PMC84430
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.8.5811
Multiple roles of ligand in transforming the dioxin receptor to an active basic helix-loop-helix/PAS transcription factor complex with the nuclear protein Arnt
Abstract
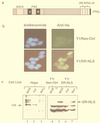
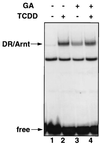
The dioxin receptor is a ligand-activated transcription factor belonging to an emerging class of basic helix-loop-helix/PAS proteins which show interaction with the molecular chaperone hsp90 in their latent states and require heterodimerization with a general cofactor, Arnt, to form active DNA binding complexes. Upon binding of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons typified by dioxin, the dioxin receptor translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus to allow interaction with Arnt. Here we have bypassed the nuclear translocation step by creating a cell line which expresses a constitutively nuclear dioxin receptor, which we find remains in a latent form, demonstrating that ligand has functional roles beyond initiating nuclear import of the receptor. Treatment of the nuclear receptor with dioxin induces dimerization with Arnt to form an active transcription factor complex, while in stark contrast, treatment with the hsp90 ligand geldanamycin results in rapid degradation of the receptor. Inhibition of degradation by a proteasome inhibitor allowed geldanamycin to transform the nuclear dioxin receptor to a heterodimer with Arnt (DR-Arnt). Our results indicate that unchaperoned dioxin receptor is extremely labile and is consistent with a concerted nuclear mechanism for receptor activation whereby hsp90 is released from the ligand-bound dioxin receptor concomitant with Arnt dimerization. Strikingly, artificial transformation of the receptor by geldanamycin provided a DR-Arnt complex capable of binding DNA but incapable of stimulating transcription. Limited proteolysis of DR-Arnt heterodimers indicated different conformations for dioxin versus geldanamycin-transformed receptors. Our studies of intracellular dioxin receptor transformation indicate that ligand plays multiple mechanistic roles during receptor activation, being important for nuclear translocation, transformation to an Arnt heterodimer, and maintenance of a structural integrity key for transcriptional activation.
Figures






References
-
- Abbott B D, Probst M R. Developmental expression of two members of a new class of transcription factors. II. Expression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator in the C57BL/6N mouse embryo. Dev Dyn. 1995;204:144–155. - PubMed
-
- Brzozowski A M, Pike A C, Dauter Z, Hubbard R E, Bonn T, Engstrom O, Ohman L, Greene G L, Gustafsson J A, Carlquist M. Molecular basis of agonism and antagonism in the oestrogen receptor. Nature. 1997;389:753–758. - PubMed
-
- Carver L A, Bradfield C A. Ligand-dependent interaction of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor with a novel immunophilin homolog in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:11452–11456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
