A novel 14-base-pair regulatory element is essential for in vivo expression of murine beta4-galactosyltransferase-I in late pachytene spermatocytes and round spermatids
- PMID: 10409768
- PMCID: PMC84431
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.8.5823
A novel 14-base-pair regulatory element is essential for in vivo expression of murine beta4-galactosyltransferase-I in late pachytene spermatocytes and round spermatids
Abstract
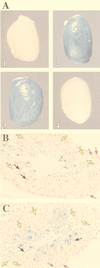
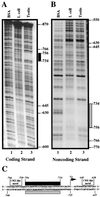
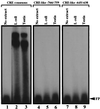
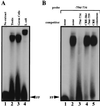
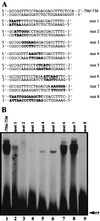
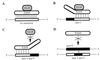
During murine spermatogenesis, beginning in late pachytene spermatocytes, the beta4-galactosyltransferase-I (beta4GalT-I) gene is transcribed from a male germ cell-specific start site. We had shown previously that a 796-bp genomic fragment that flanks the germ cell start site and contains two putative CRE (cyclic AMP-responsive element)-like motifs directs correct male germ cell expression of the beta-galactosidase reporter gene in late pachytene spermatocytes and round spermatids of transgenic mice (N. L. Shaper, A. Harduin-Lepers, and J. H. Shaper, J. Biol. Chem. 269:25165-25171, 1994). We now report that in vivo expression of beta4GalT-I in developing male germ cells requires an essential and previously undescribed 14-bp regulatory element (5'-GCCGGTTTCCTAGA-3') that is distinct from the two CRE-like sequences. This cis element is located 16 bp upstream of the germ cell-specific start site and binds a male germ cell protein that we have termed TASS-1 (transcriptional activator in late pachytene spermatocytes and round spermatids 1). The presence of the Ets signature binding motif 5'-GGAA-3' on the bottom strand of the TASS-1 sequence (underlined sequence) suggests that TASS-1 is a novel member of the Ets family of transcription factors. Additional transgenic analyses established that an 87-bp genomic fragment containing the TASS-1 regulatory element was sufficient for correct germ cell-specific expression of the beta-galactosidase reporter gene. Furthermore, when the TASS-1 motif was mutated by transversion, within the context of the original 796-bp fragment, transgene expression was reduced 12- to 35-fold in vivo.
Figures

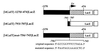
References
-
- Beyer T A, Hill R L. Glycosylation pathways in the biosynthesis of nonreducing terminal sequences in oligosaccharides of glycoproteins. III. New York, N.Y: Academic Press, Inc.; 1982. pp. 25–45.
-
- Blendy J A, Kaestner K H, Weinbauer G F, Nieschlag E, Schutz G. Severe impairment of spermatogenesis in mice lacking the CREM gene. Nature. 1996;380:162–165. - PubMed
-
- Brodbeck U, Denton W L, Tanahashi N, Ebner K E. The isolation and identification of the B protein of lactose synthetase as α-lactalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1967;242:1391–1397. - PubMed
-
- Brown T A, McKnight S L. Specificities of protein-protein and protein-DNA interaction of GABPα and two newly defined ets-related proteins. Genes Dev. 1992;6:2502–2512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
