Suppression of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1-induced cell death by 14-3-3 proteins
- PMID: 10411906
- PMCID: PMC17547
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.15.8511
Suppression of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1-induced cell death by 14-3-3 proteins
Abstract
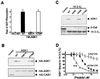
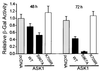
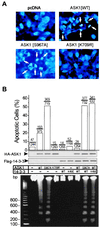
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) is a pivotal component of a signaling pathway induced by many death stimuli, including tumor necrosis factor alpha, Fas, and the anticancer drugs cisplatin and paclitaxel. Here we report that ASK1 proapoptotic activity is antagonized by association with 14-3-3 proteins. We found that ASK1 specifically bound 14-3-3 proteins via a site involving Ser-967 of ASK1. Interestingly, overexpression of 14-3-3 in HeLa cells blocked ASK1-induced apoptosis whereas disruption of the ASK1/14-3-3 interaction dramatically accelerated ASK1-induced cell death. Targeting of ASK1 by a 14-3-3-mediated survival pathway may provide a novel mechanism for the suppression of apoptosis.
Figures

References
-
- Jacobson M D, Weil M, Raff M C. Cell. 1997;88:347–354. - PubMed
-
- Rudin C M, Thompson C B. Annu Rev Med. 1997;48:267–281. - PubMed
-
- Ellis R E, Yuan J Y, Horvitz H R. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–698. - PubMed
-
- Cryns V, Yuan J. Genes Dev. 1998;12:1551–1570. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Dixit V M. Science. 1998;281:1305–1308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

